ISO guidelines, cost impacts, and real-world applications in automotive, aerospace, and medical industries. Get tips to optimize for your CNC turning service projects and save on costs.
Are you designing parts that need to fit just right, but tolerances confuse you? In CNC turning, getting tolerances wrong can lead to parts that don’t assemble, fail early, or cost too much to fix. Many beginners specify too tight or too loose, wasting time and money.
In this in-depth guide, we’ll break down CNC turning tolerances explained from basics to advanced. You’ll learn definitions, standards, influencing factors, comparisons, and practical selection strategies. We’ll include 10+ real examples, cost breakdowns, common pitfalls, and future trends.
Why care? Precise tolerances ensure reliability in critical applications. The global precision machining market reached $123.54 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit $132.93 billion in 2026, growing at 8.1% CAGR. In Lahore’s booming manufacturing sector, local shops rely on smart tolerance choices for automotive and aerospace exports. If you’re sourcing a CNC turning service or CNC turning tolerances service, this equips you to specify effectively and link to industry pages like automotive or aerospace.
By the end, you’ll confidently balance precision, cost, and performance. Let’s explore.

Defining Tolerances in CNC Turning: The Fundamentals
Tolerances specify the acceptable variation in a part’s dimensions from the nominal (ideal) value. In CNC turning—a process where a rotating workpiece is shaped by a fixed cutting tool—they ensure parts like shafts or bushings meet functional needs.
Types of Tolerances
- Linear Tolerances: For lengths, diameters (e.g., ±0.005 mm on a shaft).
- Geometric Tolerances (GD&T): Control form, orientation, location (e.g., concentricity for aligned features).
- Bilateral vs Unilateral: Bilateral allows variation both ways (±); unilateral only one (e.g., +0.01/-0).
Why explain this? Tolerances prevent over- or under-sizing, which could cause leaks in hydraulic fittings or vibrations in engine components.
How Tolerances Are Measured
Use tools like micrometers (for external diameters) or calipers. Advanced: Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) scan for 3D accuracy. In practice, inspect 10-20% of batches for quality control.
Pro Tip: Always calibrate tools before measuring—errors here can scrap entire runs.
Standard and Achievable Tolerances in CNC Turning

Standards provide baselines for consistency.
Common Industry Standards
- ISO 2768: General tolerances for machined parts. Fine (f): ±0.05 mm for 0.5-3 mm features; medium (m): ±0.1 mm for 6-30 mm.
- ASME Y14.5: U.S. standard for GD&T, emphasizing true position.
- DIN 7168: Similar to ISO, popular in Europe for turned components.
In 2026, most global shops default to ISO 2768 unless specified.
Achievable Ranges
- Standard: ±0.005 inches (±0.127 mm) – suitable for general use.
- Precision: ±0.001-0.002 inches (±0.025-0.051 mm) – for fittings.
- High-Precision: ±0.0005 inches (±0.0127 mm) – via grinding post-turning.
- Ultra-Precision: ±0.0001 inches (±0.0025 mm) – for optics or aerospace, using diamond tools.
Example: A 50 mm aluminum shaft might hold ±0.02 mm standard but ±0.005 mm precision.
Expert Advice: Test your shop’s capability with a prototype—machines vary.

Key Factors Influencing CNC Turning Tolerances
Achievability depends on multiple elements.
Material Properties
Ductile metals (aluminum, brass) machine to ±0.001 mm easily. Brittle ones (ceramics) risk chipping, widening to ±0.01 mm. Heat-sensitive plastics like ABS warp, requiring looser specs.
Why? Thermal expansion: Steel expands 0.012 mm/m per °C—control coolant to minimize.
Part Geometry and Size
Slender parts (L/D >10:1) deflect under force, loosening tolerances to ±0.005 mm. Complex features like undercuts need secondary ops.
Example: A 200 mm titanium rod holds ±0.002 mm diameter but ±0.01 mm length due to vibration.
Machine Capabilities and Tooling
Modern CNC lathes with linear guides achieve ±0.0005 mm. Worn tools add variation—change inserts every 100-500 parts.
In Lahore factories, upgraded Swiss-type lathes boost precision for export medical parts.
Environmental and Process Factors
Shop temperature swings (±5°C) alter sizes. Vibration from nearby machines adds error. Use vibration-dampening bases.
Case Study: A 2025 automotive supplier in Punjab reduced rejects 35% by stabilizing temps.
Comparing CNC Turning Tolerances to Other Machining Processes
Turning specializes in rotational symmetry.
Vs CNC Milling
Turning: Better concentricity (±0.0005 mm) for cylinders. Milling: Superior for flats (±0.001 mm) but weaker on rounds.
Table:
| Aspect | Turning Tolerance | Milling Tolerance | Best For |
| Roundness | ±0.0002 mm | ±0.001 mm | Shafts |
| Flatness | Secondary needed | ±0.0005 mm | Brackets |
| Threads | ±0.001 mm | ±0.002 mm | Bolts |
| Holes | ±0.002 mm (bored) | ±0.0005 mm | Precise fits |
Vs Grinding or EDM
Grinding: Tighter (±0.0001 mm) but slower/post-process. EDM: For hard materials, ±0.005 mm but leaves recast layer.
Choose turning for bulk removal, grinding for finish.
Real-World Applications and Examples Across Industries
Tolerances vary by sector.
Automotive Industry
Pistons: ±0.001 mm diameter for seal. Axles: ±0.005 mm length. Loose causes oil leaks; tight ensures efficiency.
Example: Ford engines use ±0.0005 mm on crankshaft journals to minimize vibration.
Aerospace Sector
Turbine shafts: ±0.0002 mm for balance. Landing gear pins: ±0.001 mm concentricity.
Boeing’s 787 parts demand GD&T for safety—failures cost millions.
Medical Devices
Hip stems: ±0.0001 mm for bone fit. Syringe barrels: ±0.002 mm for dosing accuracy.
Case: Medtronic reduced implant failures 45% with ultra-tight turning in 2025.
Electronics and Others
Connectors: ±0.001 mm for conductivity. Optical lenses: ±0.0005 mm roundness.
In Lahore’s electronics hubs, turned pins hold ±0.002 mm for PCB reliability.
Additional Examples:
5. Pump impellers: ±0.003 mm for flow.
6. Valve stems: ±0.001 mm to prevent leaks.
7. Gears: ±0.002 mm tooth profile.
8. Bearings: ±0.0005 mm inner race.
9. Fasteners: ±0.005 mm threads.
10. Hydraulic cylinders: ±0.001 mm bore.
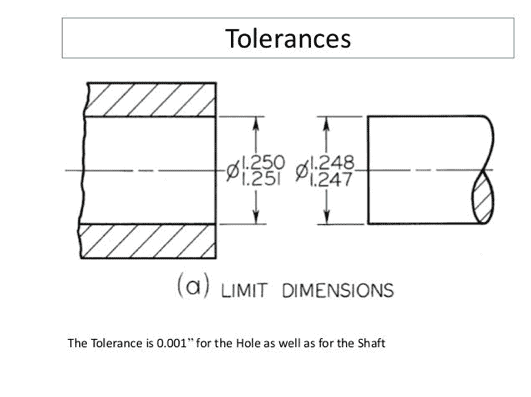
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Select Optimal CNC Turning Tolerances
Choosing the right tolerances isn’t guesswork — it’s a structured process that balances function (does the part work?), manufacturability (can the shop actually hit it?), and cost (without overpaying). Over-tightening tolerances everywhere is one of the most common ways projects blow budgets by 30–100% in 2026.
Here’s the expanded, actionable step-by-step process:
- Analyze the Function of Each Feature Start by asking: What does this dimension actually do?
- Critical mating surfaces (e.g., a shaft sliding into a bearing, a piston fitting a cylinder) → Tighten tolerances (often ±0.001 in / ±0.025 mm or better).
- Non-critical features (e.g., overall length of a non-precision shaft, outer chamfers) → Use standard/loose tolerances (±0.005 in / ±0.127 mm or ISO 2768-m). Why this first? Function drives everything. In automotive workshops, many shafts only need tight diameter on the bearing journal — the rest can be looser to save time.
- Critical mating surfaces (e.g., a shaft sliding into a bearing, a piston fitting a cylinder) → Tighten tolerances (often ±0.001 in / ±0.025 mm or better).
- Evaluate the Type of Fit Required Decide the mechanical fit between parts:
- Clearance fit (parts slide easily, e.g., rotating shaft in bushing) → Looser tolerances (±0.002–0.005 in total).
- Interference fit (press-fit, e.g., bearing pressed onto shaft) → Tighter tolerances (±0.0005–0.001 in) to control press force and avoid cracking.
- Transition fit (snug but removable) → Middle ground (±0.001–0.002 in). Use fit tables from ISO 286 or ASME B4.1. Example: For a 25 mm shaft in a bearing, H7/g6 fit often uses ±0.018 mm on hole and ±0.009 mm on shaft.
- Clearance fit (parts slide easily, e.g., rotating shaft in bushing) → Looser tolerances (±0.002–0.005 in total).
- Assess Material and Geometry Risks
- Material: Aluminum and brass hold tight tolerances easily (±0.001 in routine). Titanium/Inconel → Expect ±0.002 in due to heat/tool wear. Plastics → Loosen to ±0.005–0.010 in to avoid warp from heat/chip load.
- Geometry: Long/thin parts (L/D > 8:1) → Widen tolerances on length (±0.010 in) to fight deflection/vibration. Complex features (threads, tapers, grooves) → Add 20–30% margin or use live tooling. Lahore tip: Local shops often use bar-fed CNC lathes for high-volume steel shafts — they hold ±0.0015 in diameter reliably but loosen length to ±0.008 in.
- Material: Aluminum and brass hold tight tolerances easily (±0.001 in routine). Titanium/Inconel → Expect ±0.002 in due to heat/tool wear. Plastics → Loosen to ±0.005–0.010 in to avoid warp from heat/chip load.
- Calculate and Compare Costs Early Get quotes from 2–3 CNC turning service providers with different tolerance scenarios.
- Standard (±0.005 in): Baseline price.
- Precision (±0.001 in): +20–60% (slower feeds, better tools).
- Ultra-tight (±0.0005 in): +50–200% (extra inspection, possible secondary grinding). In 2026, batch runs (100+ parts) cut per-part cost 30–40% in Punjab shops due to lights-out operation.
- Standard (±0.005 in): Baseline price.
- Apply GD&T Where Simple ± Isn’t Enough Switch to Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing for better control:
- Use concentricity or runout on multi-diameter shafts instead of just ± diameter.
- True position on threaded holes or keyways ensures alignment.
- Profile or cylindricity on precision bores. Example: A turned pump shaft — use total runout (⊥) on the bearing surface relative to a datum axis instead of multiple ± calls. This often allows looser individual tolerances while guaranteeing function.
- Use concentricity or runout on multi-diameter shafts instead of just ± diameter.
- Prototype, Measure, and Verify Machine 3–5 prototypes first. Use micrometers, CMM, or optical comparators.
Check actual vs. specified — adjust if the shop consistently hits better/worse. 2026 reality: Many Lahore shops now offer free first-article inspection with CMM reports. - Iterate Based on Real Test Data Run functional tests (assembly, rotation, load). If failures occur → tighten critical features. If everything works with margin → loosen non-critical to cut cost. Repeat until optimized.
Quick Decision Framework (Use This Checklist Every Time)

- Budget low / high-volume? → Standard ISO 2768-m (±0.1 mm typical).
- High-stakes (aerospace, medical)? → Precision (±0.025 mm) + GD&T + CMM verification.
- Prototype phase? → Start loose, tighten only proven critical features.
- Batch production? → Ask shop for “capability study” data.
Pros of Tight Tolerances
- Higher reliability, better performance, fewer assembly issues. Cons
- +50–200% cost, 2–3× longer lead times, higher scrap risk if shop pushes limits.
Pros of Loose Tolerances
- Cheaper, faster, easier to manufacture. Cons
- Risk of poor fit, vibration, leaks, or early wear/failure.
Cost Breakdown: Impact of Tolerances on Pricing
Tolerances are one of the biggest hidden cost drivers in CNC turning. The relationship is non-linear — costs rise exponentially as you go tighter.
Typical 2026 Pricing Ranges (Lahore/Punjab Shops, Single Part Estimate)
- Standard (±0.005 in / ±0.127 mm): $20–50 per part (baseline for most jobs).
- Precision (±0.001 in / ±0.025 mm): $30–80 (+20–60%).
- Ultra (±0.0005 in / ±0.0127 mm): $50–150 (+50–200%), often requires CMM inspection (+$10–30/part).
Key Factors Driving the Increase
- Slower machining parameters: Feeds/speeds halved → cycle time doubles.
- Premium tooling: Coated carbide or CBN inserts (+$5–15/part amortized).
- Extra quality assurance: In-process gauging, 100% inspection, or CMM reports (+$10–50/batch).
- Higher scrap/rework: Pushing machine limits increases defects.
- Secondary operations: If ultra-tight needed → add centerless grinding or honing (+30–80%).
Real Example (100-Piece Batch of Steel Shafts)
- Standard tolerances: $2,000 total ($20/part).
- Precision tolerances on diameter only: $3,000 total ($30/part, +50%).
- Ultra-tight on all features: ~$6,000–8,000 total (2–4× cost).
2026 Lahore Insight
Local shops with modern Doosan/Puma lathes offer competitive rates for batches. Lights-out runs drop per-part cost 30–40% on standard tolerances. Always ask for a “tolerance vs. cost matrix” — good shops provide one.
Pro Tip: Tolerance Stack-Up Analysis Prevents Over-Specifying
Tolerance stack-up calculates how individual tolerances add up in an assembly (worst-case or statistical/RSS method).
- Example: Shaft (Ø25 ±0.01 mm) + bearing bore (Ø25 ±0.015 mm) → Worst-case clearance 0.00–0.05 mm.
- If too tight → risk binding; too loose → play/vibration.
- Use Excel, Minitab, or free tools like 3DCS for quick stacks. This often lets you loosen 70–80% of dimensions while keeping critical fits safe — saving 20–50% on machining.
Mastering this process turns tolerances from a cost sink into a competitive advantage. If you share a specific part (e.g., shaft diameter, material, fit type), I can walk through a customized example!
Common Mistakes to Avoid: 5 Key Pitfalls
- Uniform tolerances: Vary by feature—save on non-critical.
- Ignoring expansion: Account for temps in design.
- Poor drawings: Omit GD&T, leading to misinterpretation.
- Skipping prototypes: Assumptions cause costly reworks.
- Overlooking shop limits: Ask capabilities upfront.
Avoid to slash errors 25-40%.
Future Trends in CNC Turning Tolerances (2026+)

AI optimizes toolpaths for tighter holds. Hybrid machines blend turning/grinding. Nanotechnology pushes ±0.00001 mm.
Sustainability: Eco-materials demand adaptive tolerances.
Market growth: 8.1% CAGR
Key Takeaways
- Tolerances define variation; standard ±0.005 in, precision tighter.
- Factors: Material, size, machine dictate achievability.
- Industries: Automotive ±0.001 mm; aerospace ±0.0002 mm.
- Select via steps: Balance function/cost.
- Costs rise 20-100% with tightness.
- Avoid uniform specs, poor drawings.
- Trends: AI for sub-micron precision.
Conclusion
CNC turning tolerances are crucial for part success, balancing precision with practicality. From standards to factors and costs, smart choices enhance performance across industries. With 2026 market growth, adopt trends like AI for edges.
Review designs now—right tolerances transform projects.
Need guidance on your CNC turning service? Upload drawings for free quotes tailored to Lahore’s expertise. We’re here to help.
FAQs
1. What factors influence CNC turning tolerances?
CNC turning tolerances are affected by the material’s machinability, cutting tool quality, spindle speed, and machine precision. Tight tolerances require fine-tuned parameters and high-quality tools.
2. How tight of a tolerance can CNC turning achieve?
CNC turning can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm, though factors like material and machine quality may affect the final precision.
3. Why are tolerances crucial in CNC turning?
Tolerances ensure that parts fit correctly in assemblies, function reliably, and meet performance standards, especially in industries like aerospace and automotive where precision is critical.
4. How does CNC turning compare to other processes for tolerance control?
CNC turning is ideal for cylindrical parts, providing excellent control over dimensions with minimal setup time compared to other machining processes, but may require additional finishing for ultra-tight tolerances.
5. What are the main challenges in achieving tight tolerances in CNC turning?
Challenges include tool wear, material inconsistencies, thermal effects, and machine calibration. Regular maintenance and careful parameter selection help minimize these issues.