Introduction to Jig & Fixture Costing
The cost of jigs and fixtures is a crucial factor in manufacturing, influencing both production efficiency and quality. These tools, while often overlooked, are essential for ensuring accuracy and repeatability in machining, welding, assembly, and inspection processes. Understanding what drives the cost of jigs and fixtures is vital for businesses to budget correctly and make informed decisions.
What “Cost of Jigs and Fixtures” Actually Includes
The cost of designing and manufacturing jigs and fixtures includes several factors, such as materials, engineering design, machining, assembly, testing, and any additional features required for specific applications (e.g., automation, sensors). These components combine to create a comprehensive pricing structure that reflects both the complexity of the fixture and its intended use in production.
Quick Overview: Why Cost Varies Drastically
The cost of jigs and fixtures can range widely based on factors like material choice, complexity, precision requirements, and the type of fixture being produced. Simple fixtures may cost a few hundred dollars, while highly specialized or automated systems can reach tens of thousands of dollars. The more demanding the application, the higher the cost.
Who Uses Jigs & Fixtures and Why Cost Matters in Manufacturing/Contracts
Jigs and fixtures are indispensable across industries, from automotive to aerospace to medical manufacturing. For companies with high-volume production runs, investing in well-designed fixtures can significantly improve efficiency, reduce scrap, and enhance consistency. In contracts, cost management is essential to ensure that the final product meets quality standards without exceeding budget constraints.
What Determines Jig & Fixture Cost? Major Pricing Factors

1. Complexity of the Component & Design
Workpiece Geometry
The shape and size of the workpiece determine the fixture’s complexity. Simple, flat parts require less sophisticated fixtures than intricate, multi-dimensional parts. Custom fixtures for complex geometries or irregularly shaped components will incur higher design and manufacturing costs.
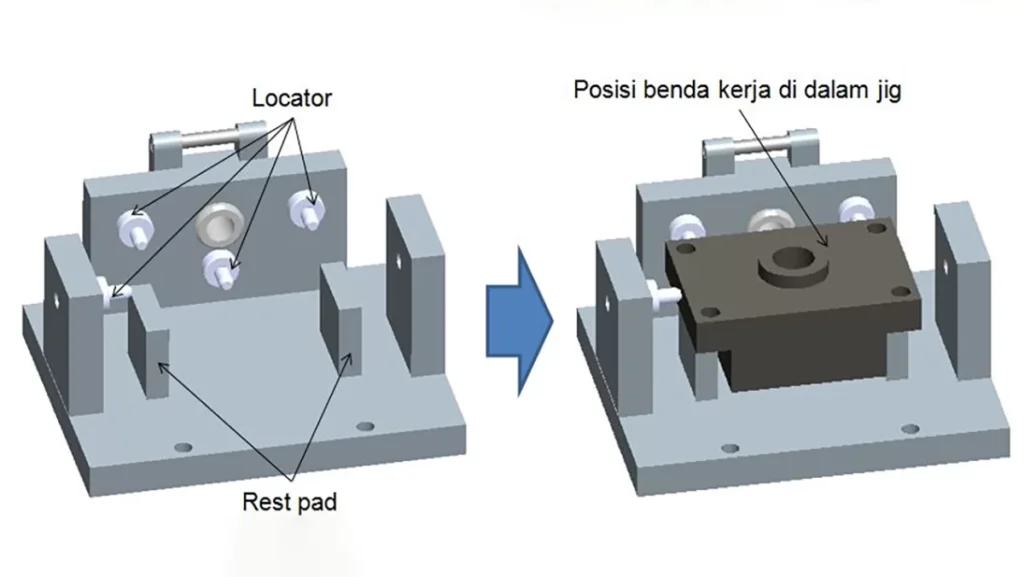
Number of Locating Points
More locating points typically mean greater precision and more complex fixture designs. The more points used to secure the workpiece, the more detailed the fixture must be.
Required Tolerances & Precision
High-precision fixtures, such as those used in aerospace or medical device manufacturing, demand more stringent tolerances, driving up the cost due to the need for specialized materials, machining processes, and quality assurance measures.
Need for Multi-Operation or Multi-Station Functionality
Fixtures that support multiple operations (e.g., drilling, milling, inspection) or multi-station setups (allowing several parts to be processed simultaneously) are more costly due to their complexity and the additional equipment required to handle multiple functions.
2. Type of Jig or Fixture Being Built
Drill Jigs vs Milling Fixtures vs Assembly Fixtures
Different types of jigs and fixtures come with varying complexities:
- Drill Jigs guide the cutting tool for drilling operations, typically simpler and less costly than fixtures for more advanced tasks like milling.
- Milling Fixtures hold the workpiece securely during milling processes and often require custom designs, increasing cost.
- Assembly Fixtures are used to position parts for assembly and may involve more advanced components, especially in high-volume settings.
Dedicated vs Modular vs Flexible Fixtures
- Dedicated Fixtures are custom-built for a specific part or production process and are typically the most expensive due to their specialization.
- Modular Fixtures offer flexibility, allowing parts to be swapped in and out, which helps reduce cost but may compromise some precision.
- Flexible Fixtures adapt to various parts but come with higher design complexity and, thus, higher costs.
Fully Manual vs Semi-Automated vs Automated Fixtures
- Manual Fixtures are less expensive but require more labor and can slow down production.
- Semi-Automated Fixtures combine manual handling with automated elements, offering a balance between cost and efficiency.
- Automated Fixtures are the most expensive but provide the highest efficiency, especially for high-volume, precision-driven tasks.
3. Material Selection
Mild Steel, Tool Steel, Aluminum, Hardened Steel, Composites
Material choice has a significant impact on cost:
- Mild Steel is inexpensive and sufficient for many general-purpose fixtures.
- Tool Steel is more expensive but offers higher strength and wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
- Aluminum is lightweight and often used for ergonomic designs but is not as durable as steel.
- Hardened Steel provides exceptional durability and precision, making it essential for high-precision applications but also a more expensive option.
- Composites offer lightweight and corrosion-resistant solutions but are typically more expensive.
Material Hardness, Wear Resistance, Heat Treatment
Materials that undergo heat treatment (e.g., hardening) for enhanced durability or wear resistance increase fixture costs due to the additional processing involved.
Cost Difference Between Temporary vs Production-Run Fixtures
Temporary fixtures are often cheaper, designed for one-time use or prototyping. In contrast, production-run fixtures are more expensive, designed for durability and high-volume operations.
4. Machining & Manufacturing Processes Required
CNC Machining Hours
The complexity of the fixture design dictates the number of CNC machining hours required. More intricate designs will require additional machining time, leading to higher costs.
EDM/Wire EDM for Precision Features
For highly precise features, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) or Wire EDM are required. These processes add significant costs but are essential for high-precision applications.
Welding & Fabrication
Fixtures that require welding or custom fabrication will have higher labor costs, depending on the material and complexity of the welds.
Surface Finishing (Anodizing, Coating, Grinding)
Finishing processes improve durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetics, but they add to the fixture’s overall cost. Anodizing and coating are common for aluminum fixtures, while grinding is used for precision surfaces.
5. Tolerance Requirements & Accuracy Level
High-precision industries, like aerospace or medical, require fixtures that maintain extremely tight tolerances. Achieving these levels of accuracy often involves more time in both the design and manufacturing phases, increasing the overall cost.
6. Number of Components & Hardware
The inclusion of custom hardware—like locator pins, bushings, clamps, and fasteners—affects cost. A fixture with numerous moving parts or specialized components will be more expensive than one with a simpler design.
7. Ergonomics & Safety Features
Fixtures often need to be designed with operator comfort and safety in mind. Features like fool-proofing mechanisms, interlocks, and ergonomic handles may increase the cost but improve safety and efficiency in the long run.
8. Design Hours & Engineering Expertise
The time and expertise required for the engineering and design phases can substantially affect the cost. CAD modeling, FEA (Finite Element Analysis) simulations, and necessary revisions all contribute to the overall expense.
9. Assembly, Testing, & Validation
Before a fixture can be used in production, it must be tested and validated for functionality. Dry-run testing and functional validation can add significant cost, particularly for complex or automated fixtures that require multiple adjustment cycles.
Jig & Fixture Cost Breakdown (Typical Cost Structure)
Engineering Design Cost
This covers the design hours for creating detailed CAD models, conducting FEA simulations, and refining the design through revisions and DFMA (Design for Manufacturability and Assembly) improvements.
Material Cost
Material costs depend on the type and quantity of materials needed, including metals, composites, and any special elements like bushings or clamps.
Manufacturing Cost
This includes all machining, welding, EDM, and surface finishing costs required to bring the fixture to life.
Assembly & Calibration Cost
This cost covers the time and labor required to assemble the fixture, align all components, and make any adjustments needed for optimal performance.
Testing & Quality Inspection Cost
Quality assurance is critical. This cost includes the use of CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines) for dimensional checks and the creation of dimensional reports to verify precision.
Extra Costs (if applicable)
- Automation Integration: If the fixture involves robotic or automated operations, integration costs are included.
- Sensors (IoT/Smart Jig): Adding sensors for real-time monitoring will increase the cost but provide valuable data for predictive maintenance and optimization.
- Spare Parts & Maintenance: Future repairs and parts replacement should be factored into long-term cost planning.
Typical Price Range for Jigs & Fixtures
- Basic Fixtures (Simple): $300–$2,000
- Medium Complexity Fixtures: $2,000–$10,000
- High-Precision or Automated Fixtures: $10,000–$30,000+ depending on complexity, material, and automation features.
How to Reduce Jig & Fixture Costs Without Compromising Quality
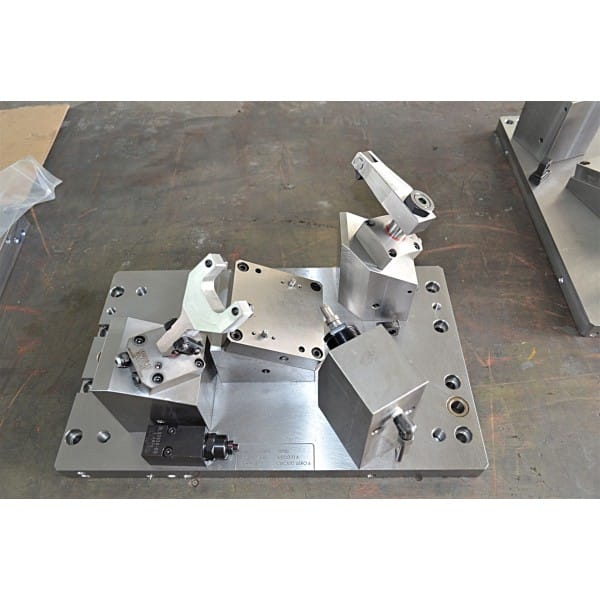

Use Standard Components Where Possible
Using off-the-shelf components for locators, clamps, and fasteners can significantly reduce costs.
Simplify Clamping & Locating Systems
Minimizing the number of complex clamping systems and optimizing the locating process can reduce design and manufacturing costs.
Use Modular Elements
Modular fixtures allow for adaptability, reducing the need for custom fixtures for each part and saving money on tooling.
Optimize for Manufacturability
Design fixtures that are easy to manufacture and assemble. Avoid over-complicating the design with unnecessary features.
Avoid Over-Engineering
Only include features that are essential for the fixture’s performance. Over-engineering increases both time and costs.
Cost Comparison: Jig vs Fixture
While jigs guide the tool and fixtures hold the workpiece, the cost of each depends largely on the complexity:
- Jigs can sometimes be more expensive due to the added complexity of guiding the tool.
- Fixtures are typically less complex but can become costly if they need to accommodate automated systems or high-precision operations.
Importance of Understanding Jig & Fixture Cost (For Businesses & Engineers)
A solid understanding of jig and fixture costs allows businesses and engineers to:
- Better Budgeting: Accurately forecast costs and manage resources.
- Faster Quoting: Quickly provide pricing for projects based on fixture requirements.
- Reducing Project Delays: Identify cost-effective designs that avoid delays in production.
- Avoiding Redesign Cycles: By understanding costs early, the risk of needing redesigns is minimized.
When Does It Make Sense to Invest in High-Cost Fixtures?
Investing in high-cost fixtures makes sense when:
- High production volume demands the efficiency and repeatability that only high-quality fixtures can provide.
- Tight tolerance manufacturing (e.g., aerospace, medical) requires fixtures that can maintain precision over time.
- Aerospace, medical, and defense applications where failure is not an option, and quality control is paramount.
- Automation & robotics integration: Automated fixtures can significantly enhance production speed and efficiency in large-scale manufacturing environments.
Conclusion
In summary, the cost of jigs and fixtures is determined by several factors, including design complexity, material selection, and the type of manufacturing processes required. Businesses must carefully consider these factors to ensure that they are investing in the right solutions for their manufacturing needs. Understanding these costs can help businesses make informed decisions, reduce waste, and optimize their production lines for greater efficiency and profitability.
FAQS
1. What factors influence the cost of jig and fixture design?
The cost of jig and fixture design depends on several factors, including material choice, complexity of the design, required precision, the type of machine being used, and the volume of parts being produced. High precision designs, custom tooling, and specialized features such as adjustable elements or integrated sensors can increase the cost.
2. Why is jig and fixture design so important in manufacturing?
Jig and fixture design is crucial for ensuring part accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency during the machining process. Well-designed fixtures minimize the need for manual adjustments, reduce cycle times, improve consistency, and enhance overall product quality, making them essential for high-volume production.
3. How do material choices affect the cost of jig and fixture design?
Material choices directly impact the cost due to factors like strength, durability, and ease of machining. For example, high-strength materials like steel or aluminum alloys might cost more than standard mild steel, but they offer better longevity and performance. The material choice depends on the type of machining process, part requirements, and expected usage.
4. What is the typical cost range for jig and fixture design?
The cost of jig and fixture design varies widely depending on complexity and material requirements. Simple designs may start at a few hundred dollars, while more complex, custom fixtures designed for specialized or high-volume production can range from thousands to tens of thousands of dollars.
5. How do the number of parts being produced affect fixture costs?
For small production runs, fixture design costs can be higher per unit because the design and setup require significant time and expertise. However, for large production runs, the cost per part decreases as the fixture design and setup costs are amortized over the larger quantity of parts produced.