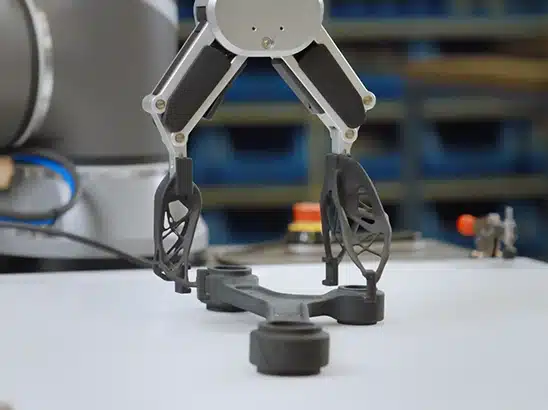
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing as of 2026, Impression 3D, or additive manufacturing, has emerged as a transformative technology for producing jigs and fixtures—essential tools that guide, hold, or position workpieces during assembly, machining, inspection, or other production processes. These tools ensure precision, repeatability, and efficiency on the factory floor..
Traditional Machining vs. 3D Printed Tooling
Traditional machining involves subtracting material from solid blocks of metal or plastic using CNC Mills, lathes, or EDM (electrical discharge machining). This process excels in producing high-strength, precise tools but is hampered by long lead times (often weeks), high costs (especially for complex geometries), and matériel waste. In contrast, 3D printing builds tools layer by layer from digital designs, enabling production in hours with minimal waste. For instance, a traditional machined fixture might cost €400 and take 35 days, while a 3D printed version could cost €10 and be ready in four days. This shift reduces dependency on external suppliers and minimum order quantities, allowing in-house production that aligns with agile manufacturing demands.
Why Manufacturing Companies Are Shifting to Jigs and Fixtures 3D Printing
The transition is driven by the need for speed, flexibility, and cost-efficiency in an era of Industry 4.0. Companies like Volkswagen have reported 89% reductions in lead times and 98% cost savings by adopting 3D printing for tooling, saving hundreds of thousands of euros annually. The technology supports rapid iteration—design changes can be implemented by simply editing a CAD file—making it ideal for prototyping and low-volume production. Additionally, Impression 3D minimizes inventory costs through on-demand production and enables the creation of lightweight, ergonomic tools that reduce operator fatigue and enhance safety. As global supply chains face disruptions, in-house 3D printing provides resilience by producing custom or obsolete parts quickly.
Where 3D Printed Jig & Fixture Use Is Skyrocketing (Automotive, Medical, Electronics)
Adoption is accelerating in high-precision sectors. In automotive, companies like Ford and MAHLE use 3D printed fixtures for assembly lines to cut downtime and costs. The medical industry leverages it for patient-specific surgical guides and orthotics, with firms like Optimus 3D customizing devices for better outcomes. Electronics manufacturing benefits from ESD-safe matériaux for handling sensitive components, as seen in applications by HP and Aereco for jigs in production lines. Overall, usage has grown from 30% of companies in 2017 to over 57% by the mid-2020s, with projections indicating near-universal adoption for certain tooling applications.
Types of Jigs & Fixtures Commonly 3D Printed
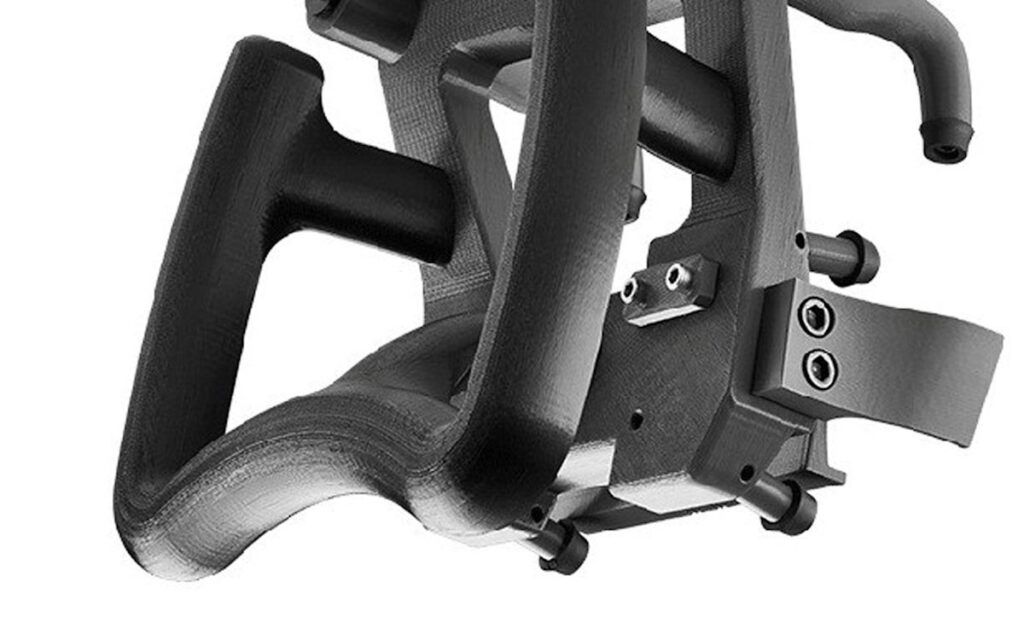

3D printing excels in producing a variety of jigs and fixtures due to its design freedom, allowing for intricate features that traditional methods struggle with. Below are common types, each optimized for specific manufacturing tasks.
Gabarits d'assemblage
These align and position components during fastening or welding, ensuring accurate placement and sturdy joints. For example, in automotive production, assembly jigs hold body panels in place, reducing errors and improving efficiency. Impression 3D allows for custom contours and lightweight designs, as demonstrated by Ford’s hook-on jigs made from Tough PLA to prevent scratches on vehicle badges.
Positioning & Locating Fixtures
These secure workpieces in precise orientations for operations like inspection or usinage. They often include datum features for reference. In electronics, positioning fixtures hold PCBs during soldering, while in aerospace, they ensure alignment for composite parts. Imprimé en 3D versions can incorporate magnetic snaps or adjustable elements for versatility.
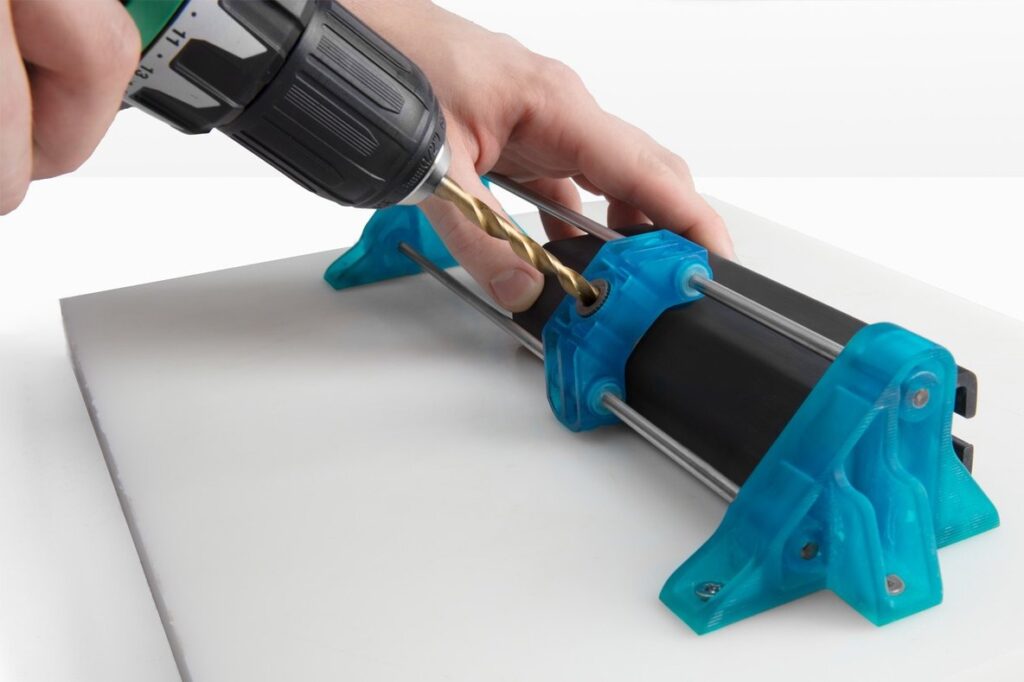
Drill Guides & Tooling Bush Holders
Drill guides direct bits to exact positions, often with bushings for repeatability. 3D printing integrates metal inserts for durability, reducing drilling time significantly—e.g., ERIKS’ custom box forage jig cut operations from minutes to seconds. These are ideal for aerospace and automotive where precision holes are critical.

Soft-Touch Clamps & Grippers
Designed with flexible matériaux like TPU, these prevent damage to delicate parts. In robotics, soft-touch grippers handle electronics without marring surfaces. Stratasys highlights their use in medical device assembly for gentle clamping.
Ergonomic Handling Tools
These tools incorporate handles and weight-optimized designs to reduce operator strain. Lattice structures in 3D prints make them lightweight yet strong, beneficial in high-volume assembly lines like those in consumer electronics.
Robotics EOAT (End-of-Arm Tooling)
Custom grippers or suction cups attached to robotic arms. Impression 3D allows for rapid customization, as in Gimatic’s robotics applications using HP MJF for competitive edge. Matériaux like carbon fiber-filled nylon provide the necessary stiffness.
When to Use 3D Printed Jigs & Fixtures
3D printing shines in scenarios where flexibility, speed, and customization outweigh the need for extreme durability.
1. Low to Medium Production Volume
- Ideal for Rapid Tooling: For runs under 100,000 cycles, 3D printing offers quick setup without tooling investments.
- Quick Iteration Cycles: Designs can be tested and modified in hours, accelerating product development.
2. Lightweight Tooling Needed
- Operators Benefit from Reduced Fatigue: Plastic prints are up to 80% lighter than metal, improving ergonomics in repetitive tasks.
3. Complex Geometry or Ergonomic Shapes
- Lattice Structures: Enable internal voids for weight reduction.
- Conformal Features Impossible with Machining: Such as curved surfaces or integrated channels.
4. When Speed Matters
- Print in Hours vs. Machining in Days/Weeks: Lead times drop by 80-90%, as in John Crane’s setup time reductions.
5. Prototyping & Early-Stage NPI (New Product Introduction)
Perfect for validating designs before full-scale production, with easy adjustments via CAD.
6. When Customization Is Required
- Personalized Locator Pins: Tailored to specific parts.
- Custom-Shaped Contact Surfaces: For unique workpiece geometries.
7. Cost Reduction Is Priority
- Significant Cost Savings for Non-Metallic Fixtures: Up to 70-98% reductions, eliminating outsourcing.
Materials for 3D Printed Jigs & Fixtures
Matériau selection is crucial for performance, balancing strength, flexibility, and environmental resistance.
PLA (Low Strength, Low Temp) For Prototyping Only
Biodegradable and easy to print, but limited to <50°C and low-stress prototypes. Ideal for quick tests but not production.
ABS General Industrial Use
Durable, impact-resistant, and affordable; suitable for indoor assembly jigs. High melting point but prone to warping if not cooled properly.
Nylon (PA12) Best All-Rounder
High ductility, heat resistance (up to 150°C), and flexibility; excellent for snap-fits and general fixtures.
Reinforced Nylon (Carbon Fiber / Glass Fiber)
- High Stiffness: 30% fiber fill boosts rigidity for high-stress tools.
- Near-Metal Replacement: Used in automotive for durable EOAT.
TPU (Flexible) — Soft-Touch Contact Surfaces

Engineering Photopolymers (Resins)
- ESD-Safe: For electronics to prevent static damage.
- High-Temperature Variants: Up to 200°C tolerance for specialized applications.
Design Guidelines for 3D Printed Jigs & Fixtures
Effective designs maximize Impression 3D‘s strengths while mitigating weaknesses.
Add Fillets + Ribs for Strength
Distribute stress evenly; use triangular or rectangular ribs in high-load areas to enhance durability without adding weight.
Use Metal Inserts Where Needed
- Threaded Inserts: For secure fastening.
- Bushes: Improve wear resistance.
- Dowel Pins: Ensure precision alignment.
Avoid Thin Vertical Walls
Opt for multiple shell layers (3-4) and consistent thicknesses to prevent warping and maintain strength.
Print Orientation Strategy (Layer Strength Optimization)
Align layers with load directions to improve adhesion and reduce weak points; critical for stress-bearing fixtures.
Design for Assembly — Hybrid (Plastic + Metal) Tooling

Incorporate modular components for easy replacement; use CAD tools like Shapr3D for rapid modeling.
Add Labeling & Color Coding
Engrave instructions or use multi-color prints for safety and usability.
Apply Soft-Touch Pads Where Required
Integrate TPU pads for non-marring contact.
Benefits of 3D Printing Jigs & Fixtures
Reduced Cost (Up to 70%)
Eliminates tooling waste and outsourcing; e.g., Jabil achieved 30-40% savings.
Faster Lead Time (Hours Instead of Weeks)
Prototypes in 24 hours vs. 8-12 weeks.
Lightweight Tooling
Reduces operator fatigue by 50-80%.
Better Ergonomics
Custom handles and shapes improve safety and productivity.
Rapid Iteration & Prototyping
Multiple versions in a day for optimization.
Flexibility in Complex Shapes
Organic designs and lattices impossible with CNC.
Design Freedom Beyond CNC
Integrated features like channels or engravings without extra steps.
Limitations of 3D Printed Tooling
Strength Limitations
Plastics fatigue under high loads; not for >100,000 cycles.
Accuracy Constraints
Tolerances of ±0.1-0.3 mm; post-processing needed for finer precision.
Surface Finish and Wear Issues
Rough finishes from SLS; wear faster than metal in abrasive environments.
Environmental Limitations (Heat, UV, Chemicals)
Degradation in extreme conditions; select matériaux carefully.
Hybrid Tooling — Best of Both Worlds
Combine 3D Printed Components + Metal Inserts
Plastic bases with metal bushes or plates for wear-prone areas; e.g., ERIKS’ jigs with press-fit tubes.
Where Hybrid Is Ideal
- High-Wear Surfaces: Metal for contact points.
- Locators Needing Precision: Dowels in plastic frames.
- Structural Elements Needing Metal: For added strength in stress zones.
Industries That Benefit from 3D Printed Jigs & Fixtures

Automobile
For assembly fixtures and drill guides; MAHLE saved thousands by consolidating parts.
Aerospace (non-critical assembly tools)
Ground support and drill guides; GKN uses for complex parts.
Électronique grand public
ESD-safe jigs for PCB handling; Aereco optimizes production.
Fabrication de dispositifs médicaux
Custom orthotics and surgical guides; Optimus 3D for patient-specific tools.
Packaging & Automation
Fixtures for line efficiency; Koch-Pac for sustainable parts.
Robotics & EOAT
Custom grippers; Gimatic gains competitiveness.
Case Studies / Examples
3D Printed Drill Jig
ERIKS developed a box drilling jig with magnetic inserts and metal tubes, reducing forage time and improving accuracy in industrial services.
3D Printed Assembly Locator
Volkswagen’s liftgate badge positioning tool, printed in Tough PLA, cut costs by 98% and lead times by 89%.
Soft-Touch Grippers for Robots
General Motors used carbon-fiber tooling for lightweight, ergonomic grippers in conveyor repairs.
Custom Bench Fixture for Electronics
Aereco created jigs with HP MJF for prototypes and final parts, eliminating outsourcing in electronics assembly.
3D Printed vs CNC Machined Fixtures Comparison Table

| Aspect | 3D Printed Fixtures | CNC-Machined Fixtures |
| Coût | Low (up to 98% savings for low volumes) | High (material waste, tooling setup) |
| Délai d'exécution | Hours to days | Days to weeks |
| Material Strength | Moderate (plastics, reinforced composites) | High (metals like aluminum, steel) |
| Précision | ±0.1-0.3 mm (post-processing improves) | ±0.01 mm or better |
| Durabilité | Good for <100,000 cycles; prone to wear | Excellent for high cycles; abrasion-resistant |
Future Trends in 3D Printed Jigs & Fixtures
High-Strength Polymers
Advancements in composites like PC+CF for near-metal performance in high-stress tools.
Metal 3D Printing for Hybrid Fixtures
Binder jetting and extrusion make metal hybrids cheaper and faster for durable fixtures.
AI-Driven Fixture Design
Generative AI optimizes designs for strength and efficiency, as in Trinckle’s software.
Automation + On-Demand Tooling
“Smart” printers with real-time adjustments enable lights-off production.
Digital Warehousing of Fixtures
Store designs digitally for instant printing, reducing physical inventory.
Conclusion
When 3D Printing Is the Right Choice for Tooling
Opt for it in low-volume, complex, or rapid-need scenarios where cost and speed are paramount.
When It Should Be Avoided
In high-heat, high-stress, or ultra-precise applications where metal excels.Importance of Hybrid Approaches for Best Performance:
Combining 3D printed plastics with metal inserts maximizes strengths, ensuring versatility and longevity in modern manufacturing.
FAQ
Are 3D printed jigs and fixtures strong enough?
Yes, for most low-to-medium volume applications; reinforced nylons provide near-metal stiffness, but they fatigue faster than metal in extreme conditions.
Which 3D printing technology is best for industrial fixtures?
FDM for cost-effective prototypes, SLS/MJF for durable nylon parts, and SLA for smooth finishes; choose based on size and strength needs.
Can 3D printed tools replace metal fixtures completely?
Not always; hybrids are often best, but for non-critical tools, yes—e.g., in automotive assembly.
How long do 3D printed fixtures last in production?
Up to 100,000 cycles with proper materials like carbon-filled nylon; depends on stress and environment.
What industries get the most benefit from 3D printed tooling?
Automotive, aerospace, medical, electronics, and robotics, where customization and speed drive efficiency.