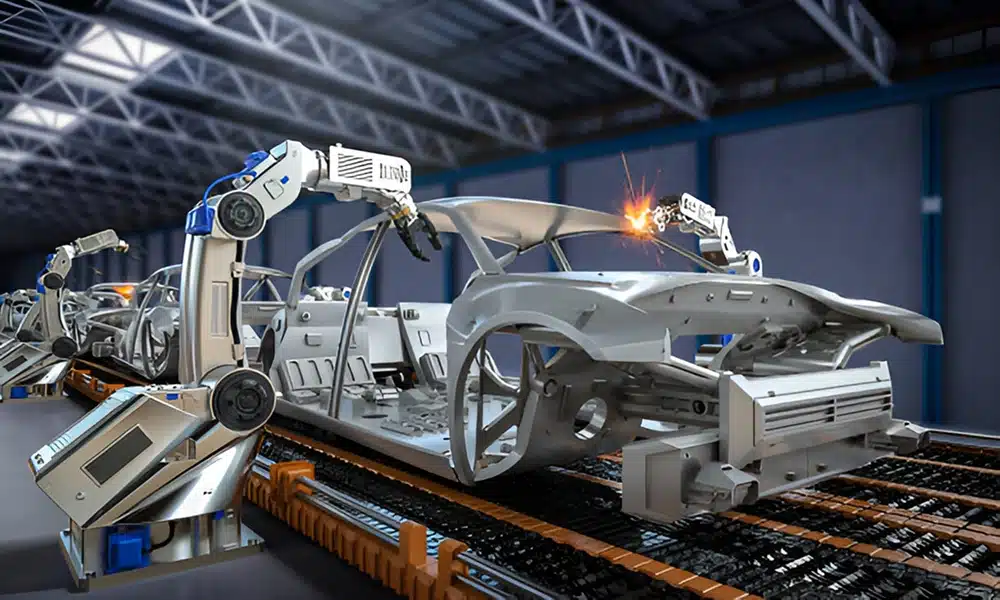
Introduction
In the world of automotive manufacturing, precision, efficiency, and consistency are key to producing vehicles that meet the highest safety and quality standards. One crucial phase in this process is Body-in-White (BIW), where all the vehicle’s sheet metal components are welded together to form the skeletal structure of the car. To ensure that each component is accurately placed and securely welded, BIW jigs and fixtures play an indispensable role in the production line.
What is BIW (Body-in-White) in Automotive Production?
Body-in-White (BIW) refers to the stage in vehicle manufacturing when the car’s frame and body are welded together before adding components like doors, hoods, bumpers, and the internal trim. It forms the rigid foundation upon which all other vehicle parts are mounted. Achieving high-quality welds in this stage is critical for the structural integrity, safety, and overall performance of the vehicle.
Importance of Jigs & Fixtures in BIW Accuracy, Rigidity & Cycle Time
BIW jigs and fixtures ensure that body components are accurately positioned, welded without distortion, and fit together perfectly. They contribute to:
- Dimensional accuracy: Ensuring parts align correctly and consistently.
- Rigidity: Providing the necessary support to withstand the stresses and heat from the welding process.
- Cycle-time reduction: Optimized fixtures reduce the setup and processing times, increasing throughput.
Difference Between Automotive BIW Jigs and General Fabrication Fixtures
Unlike general fabrication fixtures, which are often used in various manufacturing processes, BIW jigs and fixtures are specifically designed for the automotive industry. They are built for high-volume, precision assembly, where even the slightest deviation can compromise vehicle safety. These fixtures often include advanced automation features to support robotic welding and other processes critical to BIW production.
What Are BIW Jigs & Fixtures?
BIW Jig Definition
A BIW jig is a custom-designed tool used in the BIW phase to hold, position, and support the body panels during welding. These jigs ensure the parts are correctly aligned and remain fixed during the high-temperature welding process.
BIW Fixture Definition
BIW fixtures are used to support and locate body components in their correct position during manufacturing. These fixtures do not guide the welding tool, but they securely hold the parts in place, ensuring accuracy in the welding process.
Their Purpose
- Ensuring Dimensional Repeatability: Jigs and fixtures maintain consistent positioning of body panels to ensure each vehicle body is manufactured to the same high standards.
- Controlling Geometry During Welding: They help maintain the geometry of the body by holding components in precise alignment during welding.
- Reducing Build Variation: Jigs and fixtures minimize the risk of part misalignment, reducing inconsistencies that could lead to variations in the final product.
Types of BIW Jigs & Fixtures
Geo Fixtures (Geometry Control Fixtures)
Geo fixtures are used before welding to lock the geometry of the body parts. They ensure that all components, like door panels and side rails, are positioned correctly and held in place with high precision.
Respot Fixtures
These fixtures are used for welding operations that need to be completed after the geometry of the body parts has been fixed by geo fixtures. Respot fixtures allow additional welding at specific points that may have been missed or require reinforcement.
Marriage Fixtures
Marriage fixtures are used to align the chassis and body during the final assembly. They ensure that the body panels and chassis are correctly aligned, setting the stage for the final integration of the vehicle.
Checking Fixtures
These are quality control tools used to inspect the final assembly. Checking fixtures are employed to measure gap and flushness between panels, ensuring that all parts fit together with no misalignment.
Framing Stations
Framing stations are critical BIW tools used for full-body welding. They are typically located in the most critical areas of the production line and ensure that the vehicle’s frame is welded together with utmost precision.
Tooling: Grippers, Clamps & Locators
- Robotic Handling Grippers: Used to move body panels within the fixture during the assembly process.
- Pneumatic/Hydraulic Clamps: Provide strong, reliable clamping to hold body components securely.
- Precision Locator Pins: Ensure that parts are positioned in exact locations for welding.
Key Elements Used in BIW Jigs & Fixtures
Locating Pins and Rests
These elements are used to position and support body parts. Locator pins ensure the components are placed in the correct alignment, while rests provide stable support during welding.
Power Clamps / Manual Clamps
Clamps are used to hold the body parts securely in place. They can be powered (hydraulic or pneumatic) or manual, depending on the automation level of the production line.
Units (Clamp Unit, Pin Unit, Base Unit, Slide Unit)
These are specialized components in BIW fixtures that provide precise clamping, positioning, and movement. Each unit plays a role in the overall function of the fixture.
Mylar Blocks
Mylar blocks are used to provide a stable interface between the fixture and the vehicle body, ensuring minimal deformation and damage to delicate surfaces, particularly A-class surfaces.
Sensors, Pneumatics & Automation Components
Automation components such as sensors help in error-proofing by detecting misalignments, while pneumatic actuators are used for controlling clamp positions and robot movement.
Base Frames & Tool Structures
These provide the fundamental structure of the fixture, ensuring stability and rigidity during the high-stress and high-temperature welding process.
BIW Fixture Design Process (Industry Standard)
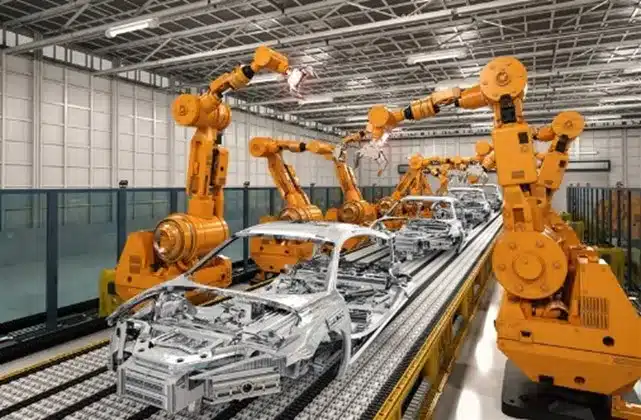

1. Requirement Gathering (VOI, GD&T, Weld Specs)
The design process starts by collecting the Voice of the Industrial (VOI), Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T), and weld specifications to understand the manufacturing requirements and constraints.
2. Concept Design (Clamp Plan, Pin Plan, Weld Plan)
A preliminary design is created, including clamp placement, pin arrangement, and welding plans, ensuring proper part alignment and optimal clamping force.
3. 3D Modeling (CATIA/Teamcenter/UG NX)
Advanced 3D modeling software like CATIA, Teamcenter, or UG NX is used to create precise digital models of the fixture, ensuring accurate representation before physical construction.
4. CAE Validation (Deflection, Stiffness, Thermal Expansion)
Finite element analysis (FEA) is used to validate the fixture design, ensuring it can withstand deflection, thermal expansion, and stresses during welding without failure.
5. Detailing & BoM Preparation
Once the design is validated, detailed drawings and a Bill of Matériaux (BoM) are created, outlining every component and material required for fixture construction.
6. Manufacturing & Assembly
The fixture is then manufactured and assembled according to the design specifications, ensuring every component is fabricated to the required standards.
7. Tryout & Buyoff
Finally, a tryout is conducted to test the fixture’s functionality in real-world conditions. Any issues are addressed before the fixture is approved for full-scale production.
BIW Welding Process Stages with Jigs & Fixtures
Underbody Welding
The underbody is one of the first parts to be welded in BIW, requiring precise alignment and support, which is provided by dedicated jigs and fixtures.
Side Body Welding
Side panels are welded next, with fixtures used to maintain precise geometry and ensure the panels are securely attached.
Roof Assembly
Fixtures for roof assembly ensure that the roof components are welded correctly, with minimal variation in shape and size.
Framing Station Welding
Framing station welding is the most critical stage, involving fixtures that provide full-body support for the assembly of the vehicle’s skeleton.
Final Weld Line
At the final weld line, all previously assembled components are welded together to form the complete body, with fixtures ensuring all parts are correctly aligned.
BIW Jigs & Fixtures Material Selection
Base Structure Materials
- Steel: Commonly used for the base frame, providing strength and durability.
- Cast Iron: Used for heavy-duty frames that require high rigidity.
Functional Components
- Aluminium : Used for lightweight components like clamps.
- Hardened Tool Steel: Used for pins and other high-wear components.
- Technical Plastics (Mylar): Used for surfaces that require minimal deformation.
Why These Materials Matter (NVH, Repeatability, Heat Expansion)
The material choice affects Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH) characteristics, repeatability of the fixture, and its ability to withstand thermal expansion during welding operations.
BIW Automation — Robots + Fixtures Integration
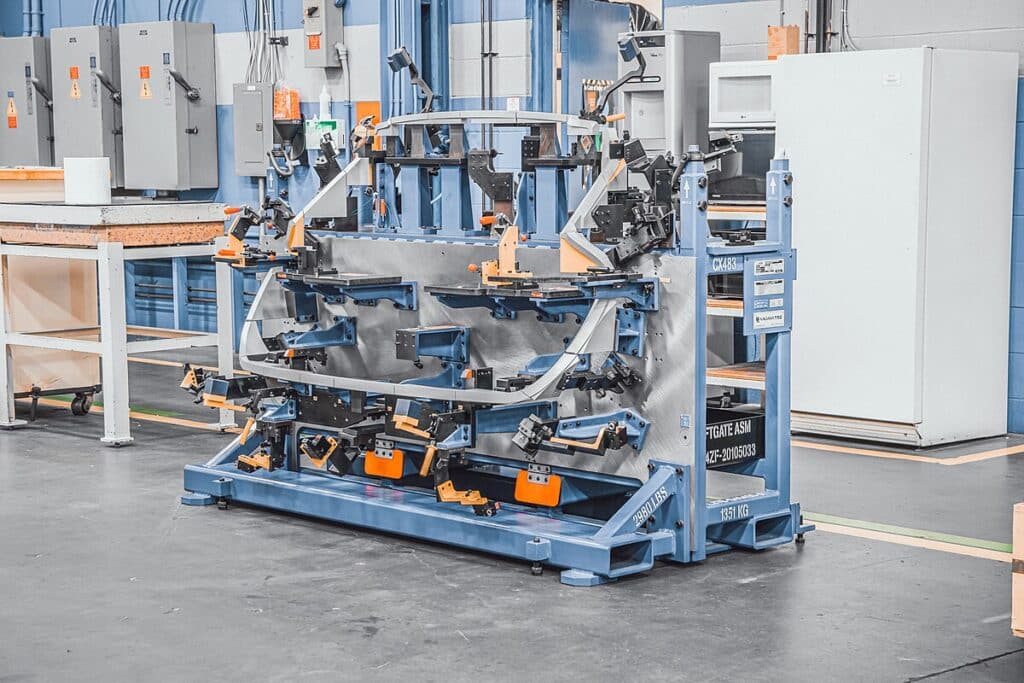

Robotic Welding Cells
Robotic cells equipped with specialized fixtures perform automated welding operations with high precision and speed.
End-of-Arm Tooling (EOAT) & Grippers
EOAT components like grippers and clamps work together with fixtures to handle body panels during welding.
Clamping Force Calculations
Accurate clamping force is critical for securing components without deformation, which is calculated based on material type and welding process.
Sensor-Based Error-Proofing (Poka-Yoke)
Sensors embedded in the fixtures detect misalignments and prevent errors, ensuring the parts are welded in the correct position.
BIW Quality Control Fixtures
CMM Fixtures
Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) fixtures are used to verify the accuracy of the welded components.
Gap & Flushness Fixtures
These fixtures are used for inspecting the gaps and flushness between body panels to ensure a perfect fit.
Attribute Checking Fixtures
Used for validating attributes like size and shape against specifications to ensure quality consistency.
Master Datums (A-B-C Coordinate Systems)
Master datums are critical for ensuring accurate positioning and alignment across all fixture components.
BIW Jigs & Fixtures — Automotive vs Aerospace
Differences in Design Philosophy
- Aérospatiale : Focuses on tighter tolerances and lower volume production, with more emphasis on high-precision and modular tooling.
- Automobile : Prioritizes cycle time, automation, and high-volume production.
Aerospace Assembly Jigs & Fixtures
Aerospace fixtures are designed for highly complex parts, like fuselage and wing assembly, often using laser-based locating systems.
Material & Accuracy Difference
Aerospace uses matériaux like invar and carbon fiber, whereas automotive BIW uses steel and aluminum.
Applications of BIW Jigs & Fixtures in Automotive
- Car Body Welding
- Welding Jigs are essential in car body welding, ensuring precise alignment and accurate positioning for consistent, high-quality welds. These jigs help maintain the integrity of the structure during welding.
- On-Line & Off-Line Robotics
Welding Jigs and fixtures work seamlessly with on-line and off-line robotics, aiding in automated welding and assembly processes with great precision. The jigs ensure that each robotic action is consistent and accurate. - Sub-Assembly Lines (Door, Hood, Fender)
Welding Jigs secure parts like doors, hoods, and fenders during sub-assembly, ensuring proper alignment and secure welding before final integration. The jigs support these parts in maintaining their correct position throughout the process. - Final Assembly Line Integration
In the final assembly line, Welding Jigs help maintain perfect part alignment, contributing to the smooth integration of the entire car body. These jigs ensure that all components fit together precisely before completion. - Quality Control and Consistency
The use of Welding Jigs in automotive manufacturing ensures high-quality production by reducing errors in alignment and weld quality, promoting consistency across the entire production process.
Challenges in BIW Jig & Fixture Design
- Distorsion thermique
- Weld Spatter
- Part Variation & Tolerance Stack-Up
- High Cycle-Time Demands
Future Trends in BIW Jigs & Fixtures
- Smart Fixtures (IoT Enabled)
- Modular BIW Tooling
- Digital Twin + Simulation
- AI-Driven BIW Weld Path Optimization
Conclusion
BIW jigs and fixtures are essential for ensuring the structural integrity, safety, and quality of automotive bodies. As technology advances, these fixtures continue to evolve with automation, digitalization, and smarter, more efficient designs. By integrating robotics, AI, and IoT technologies, the future of BIW fixture design promises to deliver even greater accuracy, productivity, and cost savings for the automotive industry.
FAQ
What is BIW in Automotive?
BIW (Body-in-White) refers to the stage in vehicle manufacturing when the vehicle’s body is assembled but not yet painted or fitted with parts like doors and windows. It involves welding all the sheet metal components together to form the vehicle’s skeleton.
What are BIW Welding Fixtures?
BIW welding fixtures are specialized tools used to hold, locate, and support the body components during the welding process. They ensure parts are correctly positioned and held in place to maintain dimensional accuracy and reduce distortion during welding.
What is the Difference Between BIW Fixtures and Aerospace Assembly Fixtures?
The primary difference lies in the design philosophy. Aerospace fixtures require higher precision and cater to low-volume, high-accuracy production, often using advanced materials like invar and carbon fiber. In contrast, automotive BIW fixtures focus on high-volume production, with a greater emphasis on cycle time and automation.
Why Are Locator Pins Important in BIW?
Locator pins are critical for ensuring that body components are precisely positioned within the fixture. They lock the part in place, ensuring consistent alignment during welding, which is essential for maintaining quality and minimizing variations in the final product.
What Software is Used for BIW Fixture Design?
Software such as CATIA, Teamcenter, and UG NX are commonly used for designing BIW fixtures. These tools allow engineers to create 3D models, perform simulations, and validate fixture designs before manufacturing to ensure accuracy and efficiency.