Introduction
Tournage CNC is one of the most precise and efficient manufacturing techniques used today. But how does Tournage CNC work, and what makes it so essential for modern industries? Whether you’re in manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, or médical sectors, understanding the Service de tournage CNC can help improve your production quality and efficiency.
In this post, we’ll break down how Tournage CNC works, its key advantages, and how it applies to various industries. By the end of this article, you’ll know everything from the basic principles to the technicalities of CNC turning services, allowing you to make informed decisions for your manufacturing needs.
What Is CNC Turning?
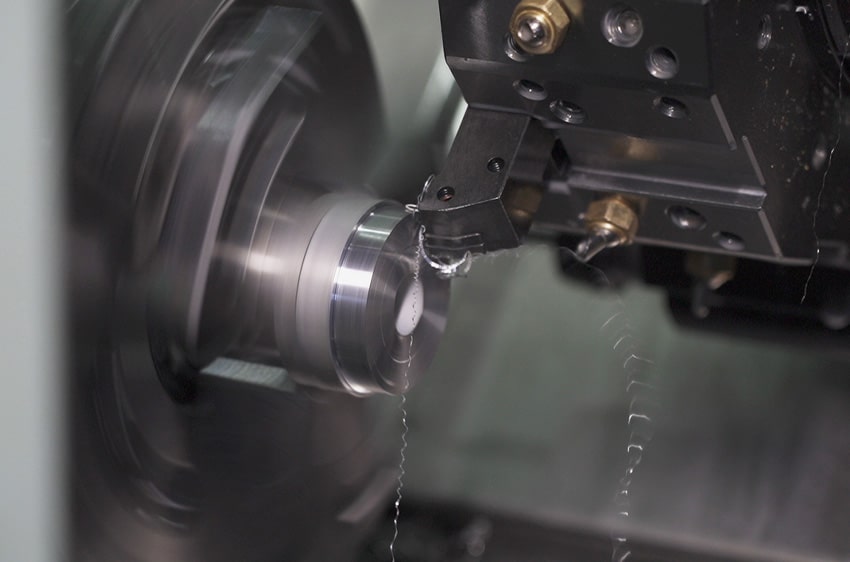

Tournage CNC (also known as CNC lathe machining) is a highly precise subtractive manufacturing process used to create cylindrical or rotationally symmetric parts. It is performed on a CNC lathe ou centre de tournage, where the workpiece rotates at high speed while stationary cutting tools remove matériel to achieve the desired shape, dimensions, and surface finish.
Core Principle and How It Works
In CNC turning:
- Le workpiece (usually a round bar, tube, or pre-formed stock of metal, plastic, or occasionally other matériaux) is securely clamped in a chuck (or collet/fixture) attached to the machine’s main spindle.
- The spindle rotates the workpiece at controlled speeds (often hundreds to thousands of RPM, depending on matériel and diameter).
- One or more cutting tools (typically single-point carbide inserts) mounted on a tool turret move linearly (and sometimes radially or along additional axes) to shear away matériel.
- The computer numerical control (CNC) system precisely coordinates tool movements, spindle speed, feed rate, and other parameters based on a programmed code (usually G-code generated from CAD/CAM software).
This differs fundamentally from Fraisage CNC, where the cutting tool rotates and the workpiece remains mostly stationary. In turning, the part spins, and the tool is primarily stationary (except for its programmed feed movements).
The process follows these main steps:
- Design — Create a 3D CAD model of the part.
- Programmation FAO — Convert the model to toolpaths and G-code.
- Machine setup — Load matériel, install tools, set offsets/zero points.
- Machining — Execute the program (often with roughing passes for bulk removal followed by finishing passes).
- Post-processing — Deburr, inspect, and sometimes apply secondary operations.
Key Components of a CNC Turning Machine
- Spindle — Rotates the workpiece (horizontal for most machines; vertical for large/heavy parts).
- Chuck — Grips the raw matériel (3-jaw, 4-jaw, collet, etc.).
- Tool turret — Holds multiple tools (8–24+ positions) for automatic tool changes.
- Contre-pointe (optional) — Supports long workpieces from the opposite end to prevent deflection.
- Axes:
- Basic: 2-axis (X = radial movement toward/away from centerline; Z = along the length).
- Advanced: 3+ axes (Y for off-center milling, C for spindle indexing/rotation, live tooling for milling/drilling while turning).
- Moderne turning centers often include live tooling, sub-spindles (for dual-sided machining without re-chucking), and Y-axis for complex features.
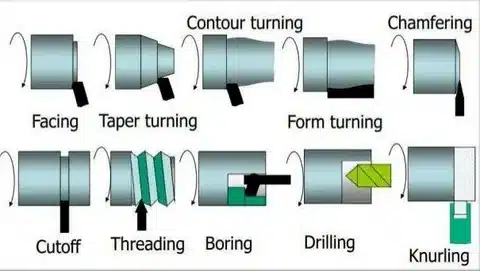
Common Types of CNC Turning Operations
Tournage CNC supports many operations, often in one setup:
- Face — Creates a flat surface on the end of the workpiece perpendicular to the axis.
- Straight/External Turning (cylindrical turning) — Reduces the outer diameter to a uniform size (roughing for fast material removal; finishing for precision and smooth surface).
- Taper Turning — Produces angled/conical surfaces (via tool angle or programmed path).
- Grooving / Parting (Cut-off) — Cuts narrow grooves or fully separates parts from the bar stock.
- Ennuyeux — Enlarges or finishes internal diameters/holes.
- Forage — Creates center holes or through holes (often with live tooling).
- Filetage — Cuts external or internal screw threads (single-point or tapping).
- Knurling — Adds textured patterns (e.g., diamond or straight) for grip.
- Chamfering / Filleting — Bevels edges or adds rounded corners.
- Shoulder / Step Turning — Creates abrupt diameter changes.
Advanced machines combine turning with milling, drilling, or even grinding in one setup.
The CNC Turning Process Explained
Understanding how Tournage CNC works requires a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
1. Material Setup
First, the raw matériel (such as metal or plastic) is secured on the CNC lathe machine. Les matériel is placed on a rotating spindle, which will spin the part at high speeds.
2. Programming
Next, the Machine CNC is programmed with the specific dimensions and shape of the part. This programming controls the cutting tool’s movements along the workpiece. The program can be modified for complex shapes or various cutting operations.
3. Cutting and Shaping
As the spindle rotates, the cutting tool moves along the matériel, gradually removing excess material. The cutting tool may move in different directions depending on the part’s geometry, shaping it into the desired form.
4. Finishing
Once the part has been shaped, it may undergo additional processes such as polishing, coating, or threading to meet exact requirements for surface finish or functionality.
Types of CNC Turning Machines
Tours CNC are available in different configurations depending on the complexity and size of the parts being manufactured. Here are a few common types:
- Vertical CNC Lathes: These are used for larger, heavier parts. The part is mounted vertically, and cutting tools are fed from above.
- Horizontal CNC Lathes: Ideal for high-precision work, these machines offer better control over matériel removal for smaller, intricate parts.
- Swiss CNC Machines: Designed for high-precision and small parts, Swiss CNC lathes excel at producing intricate, small-diameter components.
Applications of CNC Turning Across Industries
1. Aerospace Industry
In aerospace, Services de tournage CNC are crucial for producing parts that need to meet strict tolerance requirements. Components like turbine blades, fuel injectors, and landing gear parts benefit from the precision that CNC turning offers.
2. Automotive Industry
Tournage CNC is widely used in the automotive sector to create engine components, transmission parts, and suspension components. The process ensures that each part is manufactured with precision to improve performance and safety.
3. Medical Industry
Le medical field demands high-precision, reliable components such as surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics. CNC turning offers the accuracy required to manufacture these essential parts.
4. Electronics Industry
Tournage CNC is also used for manufacturing parts for electronics, such as connectors, housings, and heat sinks. The precision and reliability of Tournage CNC ensure the components work flawlessly in sensitive electronic applications.
Benefits of CNC Turning Services
Here are some of the main advantages that Services de tournage CNC offer:
1. Precision and Accuracy
CNC turning ensures extremely tight tolerances, often within a few microns. This makes it ideal for industries that require high-precision parts, such as aerospace or medical device manufacturing.
2. Increased Efficiency
Because Tournage CNC is automated, it reduces the likelihood of human error and can work 24/7, leading to higher efficiency and faster production times.
3. Cost-Effective for High Volumes
Once set up, CNC turning machines can produce large volumes of parts with minimal manual intervention. This makes it cost-effective for mass production runs.
4. Versatility
Tournage CNC can be used on a wide range of matériaux, including metals, plastics, and composites, making it a versatile choice for many industries.
Comparison: CNC Turning vs. CNC Milling
| Fonctionnalité | Tournage CNC | Fraisage CNC |
| Part Shape | Primarily cylindrical parts | Complex 3D shapes and surfaces |
| Précision | High precision for round parts | High precision for various shapes |
| Matériaux | Metals, plastics | Metals, plastics, composites |
| Process Speed | Faster for cylindrical shapes | Slower for complex parts |
| Applications | Shafts, bushings, pulleys | Complex machinery parts, molds |
How to Select a CNC Turning Service

Choosing the right Service de tournage CNC for your needs can make a significant difference in the quality and cost-effectiveness of your project. Consider the following factors when selecting a CNC turning provider:
- Experience and Specialization: Ensure the service provider has experience in your industry (e.g., aerospace, automotive).
- Machine Capabilities: Verify that the provider has the necessary equipment, such as multi-axis CNC lathes or Swiss CNC machines.
- Material Handling: Ensure that the provider can handle the specific matériaux required for your project, including any special alloys or composites.
- Assurance qualité: Look for providers that offer quality control measures to ensure each part meets your specifications.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in CNC Turning Projects
- Incorrect Material Selection: Always choose matériaux that are suitable for Tournage CNC to avoid issues with tool wear or material wastage.
- Not Specifying Tolerances Clearly: Ensure that your tolerances are clearly defined in the initial design phase to avoid parts that don’t meet your requirements.
- Overlooking Post-Processing Needs: Don’t forget to account for post-processing, such as coating or heat treatment, that may be needed to improve part functionality or appearance.
- Ignoring Maintenance: Regular machine maintenance is key to ensuring that your CNC turning service runs smoothly and consistently.
Key Takeaways
- Tournage CNC is a precise processus d'usinage used to shape cylindrical parts.
- The process involves rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool removes material to create the desired shape.
- CNC turning is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, médical, and electronics.
- The benefits include high precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for mass production.
- Proper material selection, clear tolerances, and post-processing planning are essential for successful Tournage CNC projects.
Conclusion
Comprendre how CNC turning works is crucial for anyone involved in manufacturing or production. Whether you’re looking to create custom parts or improve production efficiency, Services de tournage CNC offer a precise, cost-effective solution. By following best practices and selecting the right service provider, you can ensure that your parts are manufactured to the highest quality standards.
Need help with Services de tournage CNC? Contact us today to discuss your project needs and how we can assist you in achieving precision and efficiency in your manufacturing process!
FAQs About CNC Turning
1. What materials can be machined with CNC turning?
CNC turning works with metals (like aluminum, steel, and brass), plastics (such as PVC and ABS), and some composite matériaux.
2. Is CNC turning suitable for large parts?
Yes, CNC turning can handle large parts, especially with vertical CNC lathes, which are ideal for heavier components.
3. How fast is CNC turning compared to other machining methods?
CNC turning is generally faster than traditional machining for cylindrical parts because the process is highly automated and can run continuously.
4. What is the difference between CNC turning and CNC milling?
CNC turning primarily creates cylindrical parts by rotating the workpiece, while CNC milling involves removing material using a stationary cutting tool to create more complex shapes.
5. How accurate is CNC turning?
CNC turning can achieve high precision, often within a few microns, making it ideal for industries that require tight tolerances.