Introduction
Modern manufacturing depends on precision technology that transforms raw materials into finished components quickly. Laser cutting services have revolutionized production by offering speed and accuracy traditional methods cannot match. This technology uses concentrated energy beams to cut through metals, plastics, and other materials with remarkable precision.
Businesses choose laser cutting because it eliminates expensive tooling and setup costs. Design changes happen in software rather than on the factory floor. From prototype development to mass production, this method delivers consistent results meeting tight specifications while supporting just-in-time manufacturing.
What is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting employs focused energy beams to separate materials along programmed paths. The technology directs high-powered light through optics that concentrate the beam to a tiny point. When this focused laser beam contacts material, intense heat causes immediate melting or vaporization.
The automated nature ensures every part matches design specifications exactly. Most online laser cutting providers complete orders within days because the process requires no custom tooling or lengthy setup procedures. Companies processing hundreds of components get identical results from first piece to last.
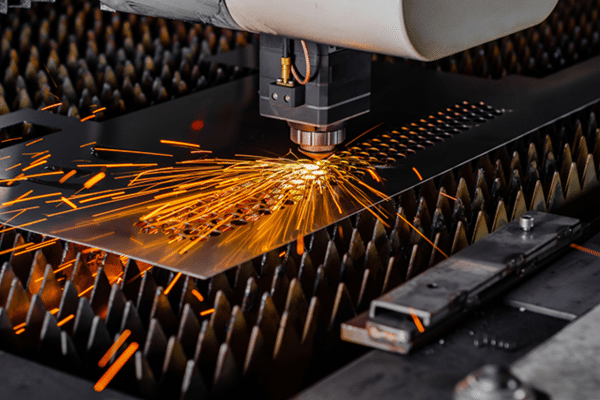

Cutting vs Engraving vs Marking
Three distinct processes serve different manufacturing needs. Cutting penetrates completely through material thickness to separate individual pieces from sheet stock. The laser beam cuts through the entire depth, creating parts ready for assembly.
Engraving removes only surface layers to add decorative patterns, text, or identification marks. This technique creates recessed areas while leaving the base material intact. Marking alters surface appearance without removing significant material through heat-induced chemical changes.
How Does Laser Cutting Work?
Production begins when designers create vector artwork in CAD software. These digital files contain precise coordinates defining every cut path and feature location. Operators upload the CAD file to control software that translates designs into machine commands.
A CNC machine positions the cutting head above the workpiece following programmed coordinates. As the focused laser beam strikes the surface, concentrated energy raises temperature beyond the melting point. Metal liquefies along the cut path while plastics vaporize cleanly. Pressurized assist gas blows through the cutting zone simultaneously, removing molten material and preventing oxidation.
Key Components of a Laser Cutter
Industrial systems integrate multiple technologies working together. The laser source generates the primary beam using either gas excitation or fiber optics. An optical system directs this energy through mirrors or fiber cables to the cutting head. Motion control systems move the head or workpiece table with precision measured in thousandths of an inch.
Cooling systems prevent overheating that could damage sensitive components. Exhaust systems remove fumes and particulates, keeping the work area clear and protecting operator health. The control computer manages all functions while monitoring system status.
Focus, Alignment, and Machine Settings
Achieving quality results demands proper equipment setup. Beam focus determines power density at the cutting point, with focal length varying by material thickness of the material. Misaligned optics scatter energy and create uneven cuts with rough edges.
Operators adjust multiple parameters for each job. Power output controls how much energy reaches the material. Cutting speed determines how long the beam stays in one location. Gas pressure affects material removal and edge oxidation. Steel needs different settings than acrylic or wood because thermal properties vary significantly.
Types of Laser Cutters
| Laser Type | Best Materials | Power Range | Maximum Thickness |
| CO₂ Lasers | Wood, Acrylic, Plastic | 40W – 400W | 20mm non-metal |
| Fiber Lasers | Steel, Aluminum, Brass | 500W – 12kW | 25mm metal |
| Diode Lasers | Thin Wood, Leather | 5W – 40W | 5mm organic |
CO₂ Lasers
These machines generate beams through electrically excited carbon dioxide gas mixtures. Many custom laser cutting service operations use CO₂ technology because it handles diverse materials with excellent edge quality. The systems work particularly well on plastics, producing polished edges that need no additional finishing.
Wood cuts cleanly with minimal charring when parameters are optimized. Lower equipment costs make this technology attractive for shops serving varied customer needs across multiple material types.
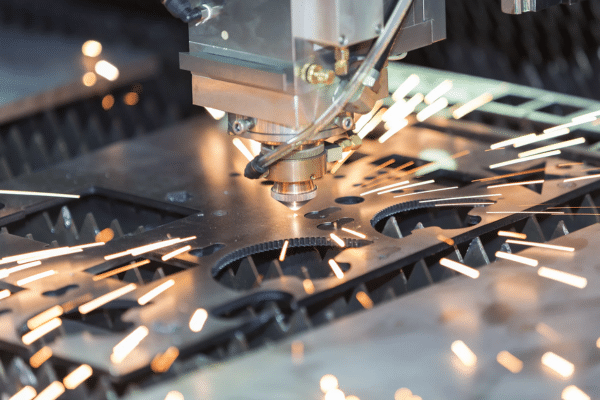
Fiber Lasers
Fiber laser technology dominates metal laser cutting services through superior performance on reflective materials. These systems generate beams within optical fibers doped with rare earth elements. The shorter wavelength absorbs strongly into metals like steel, stainless steel, and 6061 aluminum.
Fiber lasers deliver higher power density in smaller beam diameters compared to CO₂ alternatives. This concentration cuts through thick metal plates while maintaining narrow kerfs and tight tolerance. Energy efficiency exceeds gas lasers significantly, reducing operational costs over the equipment lifetime.
Diode Lasers
Compact diode systems provide affordable entry points for small operations and hobbyists. These lasers work adequately for engraving and cutting thin materials like paper, thin wood, and leather. Power output remains limited compared to industrial alternatives.
The technology suits prototype development and craft production where material thickness stays minimal. However, diode lasers cannot process metals or thick plastics effectively.
Tube Laser Cutting Machines
Specialized equipment processes cylindrical profiles and structural tubes without secondary operations. The machine rotates workpieces while the cutting head moves along multiple axes simultaneously. This approach cuts, drills, and notches tubes in single setups.
Manufacturers use tube laser cutting for furniture frames, automotive exhaust components, and architectural railings. The technology handles round pipes, square tubes, and complex structural shapes with equal ease.
Materials for Laser Cutting
Common Materials You Can Cut or Engrave
Metal parts production relies heavily on fiber laser technology. Carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum account for the majority of sheet metal fabrication. Brass and copper require higher power levels due to thermal conductivity but still produce quality results. Most metal cutting service providers handle materials from thin gauge sheet up to 25mm thick plate.
Plastics including acrylic and polycarbonate cut cleanly with polished edges that often need no finishing. Wood products like plywood, MDF, and solid hardwoods process easily with proper ventilation. Birch plywood remains popular for architectural models and decorative items.
Materials That Should Not Be Laser Cut
Certain substances create dangerous conditions or damage equipment. PVC and vinyl release chlorine gas that corrodes machine components while posing serious health risks. Polycarbonate produces toxic fumes despite being technically cuttable. Fiberglass generates harmful particles and damages mirrors and lenses.
Applications of Laser Cutting
Hobbies and Crafts
Enthusiasts create detailed jewelry, miniatures, and decorative items using online custom laser cutting services providers. The technology enables complexity impossible with hand tools. Model builders produce architectural miniatures with accuracy that enhances realism. The ability to order a single custom part makes experimentation affordable for hobbyists.
Small Business Production
Small manufacturers rely on laser cutting for rapid prototyping and limited production run quantities. Sign companies produce dimensional letters and decorative panels from acrylic and metal. Electronics firms create precise enclosures and brackets. Product developers iterate designs quickly because changes require only file modifications.
Industrial Applications
Large-scale operations integrate CNC laser cutting services into automated production lines. Automotive suppliers manufacture brackets, mounting plates, and structural components by the thousands. Appliance makers produce housing panels and internal parts. Aerospace industry relies on laser metal cutting for aluminum and titanium components where tight tolerances ensure proper fit.
Tube Laser Cutting Applications
Furniture manufacturers cut frames from round and square tubes. The process handles notching, angle cutting, and hole placement in single operations. Automotive exhaust systems benefit from precise tube cutting and flange hole patterns. Architectural firms specify laser cut metal tubes for railings and facade supports.
Getting Started With Laser Cutting
Step 1 Should You Buy or Use a Service?
Community makerspaces offer equipment access for hourly fees without ownership commitment. Schools and universities often maintain laser cutters for student projects. Outsourcing to laser cutting services eliminates all equipment investment and maintenance concerns.
Yicen Precision delivers high quality laser cut parts through streamlined online ordering systems. Users upload design file content and receive instant quotes showing exact costs before committing. Professional shops handle everything from single prototypes to production runs of thousands.
Buying equipment makes sense when production volume justifies investment. Desktop machines start around $3,000 while industrial units exceed $100,000. Ownership requires dedicated space, proper ventilation, trained operators, and ongoing maintenance.
Step 2 Designing for Laser Cutting
Software creates vector files controlling cutting operations. Popular CAD programs include AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and free alternatives. Designs must use vector formats rather than raster images. Most systems accept DXF or SVG files as standard interchange formats.
Proper file preparation accounts for kerf width removed during cutting. Designers must compensate for this removal when parts require precise cutting dimensions. Professional laser cutting services offer design guidelines ensuring files produce intended results.
Step 3 Preparing the Machine
Material placement affects results significantly. Stock must sit flat against the table to maintain consistent focal distance. Operators secure workpieces to prevent movement during cutting process operations.
Settings selection requires understanding material properties. Power output, cutting speed, and assist gas pressure must match material type and thickness. Many machines store parameter libraries for common materials.
Step 4 Running the Cut
Test cuts on scrap material verify settings before processing actual parts. Sample pieces reveal any problems with focus, alignment, or parameter selection. Active monitoring during production catches problems before significant damage occurs.
Materials can ignite if settings prove incorrect or ventilation fails. Fire suppression equipment must remain within immediate reach. Never leaving machines unattended prevents minor issues from becoming serious problems.
Benefits of Laser Cutting Services
Precision and Smooth Edges
Laser cutting services achieve exceptional accuracy with tolerances reaching ±0.1mm on quality equipment. The focused laser beam creates narrow kerfs enabling tight nesting patterns. Sharp internal corners and complex curves emerge cleanly without radius limitations.
Smooth edges often require no additional finishing operations. The cutting process produces clean surfaces free from burr that plague punching operations. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology, laser systems maintain dimensional consistency better than mechanical alternatives across production runs.
Speed and Repeatability
Automated systems process parts faster than manual operations while maintaining perfect consistency. The first piece matches the thousandth exactly as specified because computer control eliminates human variation. Complex geometries take similar time to simple shapes since programming handles all complexity digitally.
Handling Complex Designs
Laser cutters can cut intricate nested patterns and impossibly tight internal radii. The process creates features smaller than any drill bit or punch. Design complexity adds no extra cost because programming handles everything digitally.
Minimal Waste and Eco-Friendly
Narrow kerf widths reduce material waste substantially. Nesting software arranges parts efficiently on sheet metal stock to maximize yield. Laser cutting produces no hazardous coolants, oils, or chemicals requiring special disposal. Scrap material remains clean and recyclable.
Cost-Effectiveness
Laser cutting offers a cost-effective manufacturing solution for quantities from one to thousands. Design changes require only file modifications rather than new die fabrication. Instant online quoting systems provide complete price transparency. Companies get an instant online quote showing material costs and processing time within minutes.
No Tool Wear
Physical cutting tools are dull and require regular replacement adding cost and downtime. Laser beams never wear out over equipment lifetime. Maintenance focuses on optical cleaning rather than consumable tooling. Quality of parts remains constant throughout equipment life.
Choosing the Right Laser Cutting Services Provider
Laser Technology Used
Different providers specialize in specific technologies. Fiber systems excel at metal laser cutting applications. CO₂ lasers handle a wide range of materials including plastics and wood. Yicen Precision operates advanced fiber lasers optimized for metal production delivering high quality laser cut parts that demanding applications require.
Material Capability and Thickness
Service capabilities vary by equipment specifications. Some shops process only sheet metal parts while others handle diverse categories. Maximum thickness depends on laser high power output and technology type. Fiber systems typically cut metal up to 25mm while CO₂ lasers handle acrylic to 20mm effectively.
Accuracy and Tolerances
Standard laser cutting achieves ±0.1mm to ±0.25mm depending on equipment quality. Understanding realistic capabilities helps designers set appropriate dimensions. Dimensional accuracy directly affects assembly fit and product function.
File Compatibility and Design Support
Professional services accept standard formats including DXF, DWG, and PDF files with vector content. Technical support should help customers prepare files correctly. Identifying potential problems before production starts saves time and material.
Turnaround Time and Pricing
Production schedules vary among providers based on equipment capacity. Rush services deliver faster results at premium pricing. Standard turnaround typically ranges from three days to two weeks. Instant pricing systems enable quick cost comparisons. Many shops offers instant quotes providing pricing within minutes of file upload.
Customer Reviews and Portfolio
Previous customer experiences provide valuable insight into service quality. Portfolio examples demonstrate capability with various materials and design complexities. Companies used by Apple demonstrate proven reliability at demanding quality levels.
Safety in Laser Cutting
Ventilation and Fume Extraction
Adequate ventilation removes harmful fumes generated during processing. Most laser cutting materials produce smoke containing potentially toxic compounds. Industrial exhaust systems maintain negative pressure pulling fumes away from operators.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration provides specific guidelines for workplace ventilation in laser operations. Proper systems protect operator health while maintaining visibility during cutting.
Protective Gear and Goggles
High powered lasers generate intense light that permanently damages eyes. Protective eyewear rated for specific wavelengths blocks harmful radiation. Never viewing the laser beam directly remains critical even when wearing safety glasses.
Heat-resistant gloves protect hands from hot materials. Fire-resistant clothing reduces burn risk during material handling.
Machine Maintenance and Fire Prevention
Regular cleaning removes flammable residue accumulating in cutting areas. Inspection of gas lines, electrical connections, and cooling systems prevents equipment failures. Fire extinguishers rated for electrical and metal fires must remain immediately accessible.
Conclusion
Laser cutting services deliver precision manufacturing solutions across industries with accuracy traditional methods cannot match. The technology handles materials from thin foils to thick plates economically. Understanding equipment types, material compatibility, and design requirements leads to successful outcomes. Safety practices protect operators while proper technique ensures quality results meeting modern manufacturing standards.
FAQs
What is the difference between cutting, engraving, and marking?
Is laser cutting expensive?
What thickness can a laser cutter handle?
Can laser cutting be used on all types of metal?
What safety precautions are needed for laser cutting?
Citations
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration. “Laser Safety Guidelines.” OSHA.gov. https://www.osha.gov/
- National Institute of Standards and Technology. “Precision Manufacturing Standards.” NIST.gov. https://www.nist.gov/
- “Laser Cutting Technology.” Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laser_cutting
- U.S. Department of Energy. “Advanced Manufacturing.” Energy.gov. https://www.energy.gov/
- Yicen Precision. “CNC Laser Cutting Services.” https://yicenprecision.com/