Introduction
Metal manufacturing demands precision, speed, and cost control. Die casting delivers all three by injecting molten metal into steel molds under high pressure—producing complex parts with excellent surface finish. When paired with CNC Machining Services, you get unmatched accuracy, tighter tolerances, and superior final results.
Over 17 million tons of die cast parts ship globally each year. Industries from automotive to electronics rely on this proven metal casting process for high-volume production needs.
Understanding when die casting service makes sense versus alternatives helps manufacturers avoid costly mistakes. Material selection, tolerance requirements, and production volume all determine whether custom die casting fits project needs.
This guide examines real applications with specific data. Boeing requires aerospace-grade tolerances. Ford specifies exact specifications for automotive parts. Samsung demands tight tolerances for aluminum parts in consumer electronics. These examples show how die casting capabilities serve diverse industries.
Understanding Die Casting Fundamentals
The die casting process forces molten metal into precision tool cavities at 10,000-30,000 PSI. Temperatures exceed 1,200°F as aluminum, zinc, or magnesium transforms from liquid to solid in seconds.
Two machine types handle different casting alloys. Hot chamber machines melt and inject automatically—perfect for zinc die casting and low melting point metals. Cold chamber die casting uses separate furnaces for aluminum casting where higher temperatures would damage integrated systems.
How Gooseneck Casting Works
Hot chamber systems use a gooseneck mechanism submerged in molten metal. Hydraulic pressure forces liquid through the injection system into the mold cavity. Cycle times run 30-60 seconds for small zinc die cast parts.
Cold chamber casting requires manual ladling. Metal melts separately, transfers to the injection chamber, then high pressure die casting forces material into the die. This type of die casting suits aluminum and zinc alloys requiring higher processing temperatures.
Material Selection for Die Cast Components
Aluminum die casting alloys dominate at 65% market share per 2024 NADCA data. A380 and A383 provide excellent strength-to-weight ratios for automotive parts. Zinc offers superior precision for detailed features under 1mm. Magnesium delivers lightweight solutions for aerospace applications.
Each casting alloy serves specific needs. Tesla uses aluminum for motor housings requiring thermal conductivity. Apple specifies zinc die casting for MacBook frames needing tight tolerances. Boeing requires magnesium where weight reduction matters critically.
Key Advantages of High Pressure Die Casting
Speed separates die casting from other casting methods. Certified die casting machines ranging from 250 to 2,800 tons produce 400-600 metal parts daily. A Michigan transmission supplier cut production time 88%—from 8 hours to 52 minutes per batch using high-volume production methods.
Die casted parts emerge with excellent dimensional accuracy. Standard tolerances hold ±0.1-0.3mm across thousands of die cast components. Honda Tier 1 suppliers maintain these tight tolerances for safety-critical automotive parts without secondary operations.
Surface Quality and Finishing Services
High-quality surface finish comes directly from precision die casting. Roughness measures 1.6-3.2 Ra—smooth enough for many applications without grinding or polishing. Samsung ships laptop housings straight from aluminum die casting machines without additional finishing services.
This eliminates 70% of post-processing costs versus rougher casting processes. Custom metal parts often need only powder coating or anodizing rather than extensive machining. In-house precision machining handles critical features when tighter specifications apply.
Mechanical Strength of Metal Die Castings
High pressure creates dense crystalline structures. Aluminum die casting alloys reach 280 MPa tensile strength—suitable for structural automotive components. The injection process eliminates porosity in critical areas, producing die castings that meet aerospace standards.
Ford documents 35 die cast parts per F-150 truck. These complex metal parts reduce vehicle weight 68 kilograms versus fabricated alternatives. Material efficiency runs 95-98% with minimal waste compared to cnc machining that removes 40-70% as chips.
Critical Limitations of Die Casting Manufacturing
Tool costs create barriers for low-volume projects. Simple dies start at $15,000. Complex multi-cavity precision dies reach $150,000. Break-even typically occurs at 1,500-2,000 units where custom die casting becomes economical versus alternatives.
Gas entrapment during injection creates internal voids. These defects weaken die cast part strength 15-30% in affected areas. Medtronic discovered this producing surgical instruments—standard methods failed leak tests until implementing vacuum-assisted die casting solutions.
Material Constraints in Metal Casting
Only non-ferrous metals work reliably. Aluminum and zinc dominate because steel’s 1,500°C melting point destroys die casting machines rapidly. An Ohio manufacturer attempted iron casting—die life dropped from 200,000 to 18,000 cycles before catastrophic tool failure.
Like aluminum, magnesium works well despite reactive properties. Copper alloys suit electrical components but reduce die life 40% versus zinc die casting. Each casting material requires specific expertise from your die casting manufacturer.
Volume Requirements for Die Casting Products
Below 1,000 annual units, other manufacturing services cost less. A medical device company calculated $62 per part for 500-unit die casting service versus $38 with cnc machining over five-year total cost.
High-volume production drives economics. General Motors amortizes tooling across millions of aluminum parts annually. Their supply chain requires die casting capabilities handling repeatable quality at scale—something injection molded plastics can’t match for metal components.
Comparing Die Casting to Alternative Processes
Each metal casting process serves different project needs. Sand casting handles large parts cheaply but delivers rough surfaces. Investment casting works beautifully for low volumes under 500 units. Forging creates maximum strength but struggles with complex geometries.
| Process | Best Volume | Tolerance | Surface Finish | Tooling Cost |
| Die Casting | 1,500+ units | ±0.1-0.3mm | Excellent (1.6-3.2 Ra) | $15K-$150K |
| Investment Casting | 50-500 units | ±0.3-0.5mm | Good (3.2-6.3 Ra) | $3K-$15K |
| Sand Casting | 1-100 units | ±0.5-2mm | Poor (6.3-25 Ra) | $500-$5K |
Hybrid Manufacturing Approaches
Combining casting methods with cnc machining optimizes results. Cast the basic shape of the part, then machine critical features. Tesla uses this for motor housings—aluminum die casting for the body with precision machining on bearing surfaces to ±0.02mm.
Costs drop 45% versus full cnc machining. The die casting design eliminates 80% of material removal while maintaining exact specifications where needed. This approach suits industries requiring both high-volume production and precision components.
Selecting Quality Die Casting Services
ISO 9001:2015 certification indicates established quality systems. Industry-specific standards matter more—IATF 16949 for automotive, AS9100 for aerospace applications. Request certificate numbers and verify with issuing bodies before committing to any die casting project.
Experience across the United States varies dramatically. A provider serving automotive clients 15+ years understands tight tolerances and supply chain requirements. Apple’s MacBook suppliers need demonstrated aerospace-grade capabilities—general metal die casting shops can’t meet specifications.
Evaluating Die Casting Capabilities
Machine range determines flexibility. Quality online die casting services operate equipment from 400 to 2,800 tons. This handles custom die cast parts from 50 grams to 25 kilograms efficiently.
In-house capabilities matter critically. Die casters offering cnc machining, finishing services, and assembly under one roof cut lead times significantly. Honda suppliers must deliver finished automotive parts, not raw metal castings requiring secondary operations.
Design for Manufacturing Support
Experienced die casting manufacturer teams prevent expensive mistakes. Engineers analyze the casting design before creating precision dies—catching issues like insufficient draft angles or difficult-to-fill sections. This consultation saves 20% on tool costs.
Raytheon requires detailed DFM analysis for aerospace components. Their specifications demand verification that die casting is suitable for each application. The casting works only when design, material, and process align properly.
Cost Analysis for Die Casting Projects
Initial investment centers on tooling. Budget $15,000-$25,000 for simple dies. Complex multi-cavity tools requiring precision components cost $60,000-$100,000. Add $18,000-$35,000 for prototype dies validating the die casting design.
Part weight drives production expenses. Aluminum parts under 100 grams cost $1.80-$3.20 per unit at 5,000+ volume. Components weighing 200-500 grams run $4.50-$9.50 each. Material, machine time, and energy all factor into pricing.
Long-Term Investment Considerations
Dies wear through repeated thermal cycling. Aluminum casting typically yields 180,000-280,000 cycles before refurbishment. Zinc extends to 450,000+ shots. Copper reduces life to 120,000-150,000 cycles due to higher processing temperatures.
Calculate replacement timing: annual production divided by die life. Running 40,000 custom metal parts yearly means refurbishment every 4-7 years. Budget $10,000-$28,000 for die repair depending on damage severity.
Industry Applications of Die Cast Products
Automotive consumed 54% of global casting parts output in 2024. Engine blocks, transmission cases, and structural brackets represent primary uses. Ford’s F-150 uses 35 aluminum die casting components per vehicle—reducing weight 68 kilograms versus traditional fabrication.
Electronics grew 12% year-over-year per industry analysis. Samsung relies on custom die solutions for smartphone frames. Thermal management requirements make aluminum ideal—excellent conductivity dissipates processor heat that injection molded plastics can’t handle.
Aerospace and Medical Applications
Weight-critical applications demand magnesium die casting capabilities. DJI drone housings achieve 45% weight reduction versus aluminum while maintaining structural integrity. These high-precision metal components meet demanding aerospace specifications.
Medical device manufacturers adopt die casting increasingly. Biocompatible aluminum alloys meet FDA requirements for surgical instruments. Medtronic produces imaging equipment housings using certified die casting processes with documented traceability.
Common Mistakes in Die Casting Manufacturing
Missing draft angles causes ejection problems. Vertical surfaces need 1-3 degree tapers for reliable release. A Connecticut manufacturer redesigned tooling after parts stuck—costing $12,000 rework plus 5-week delay. Specify drafts clearly in the casting design phase.
Over-specifying tolerances inflates costs unnecessarily. Requesting ±0.05mm throughout when ±0.2mm functions adequately adds 30% to expenses. Tighten specifications only on mating surfaces and critical dimensions.
Material Selection Errors
Choosing wrong casting alloys wastes money. Zinc provides better accuracy for detailed features and walls under 1mm. Aluminum suits larger structural components needing strength-to-weight ratios. A Texas manufacturer switched from aluminum to zinc for electronics housings—dimensional stability improved 40% while costs dropped 15%.
Like aluminum, magnesium requires expertise. Reactive properties demand careful handling and specialized die casting machines. Contact experienced die casters before specifying magnesium for any die casting project.
Inadequate Prototyping Strategy
Skipping validation risks tooling failures. Progressive testing catches errors: 3D print first ($800-$2,000), then cnc machining metal prototype ($2,500-$7,500), finally prototype die casting ($18,000-$32,000). Each phase identifies issues before expensive production commitment.
Boeing follows this religiously for aerospace parts. Early detection through online die casting services consultation prevents million-dollar mistakes. The shape of the part must work before investing in production-grade precision dies.
Quality Control for Metal Die Castings
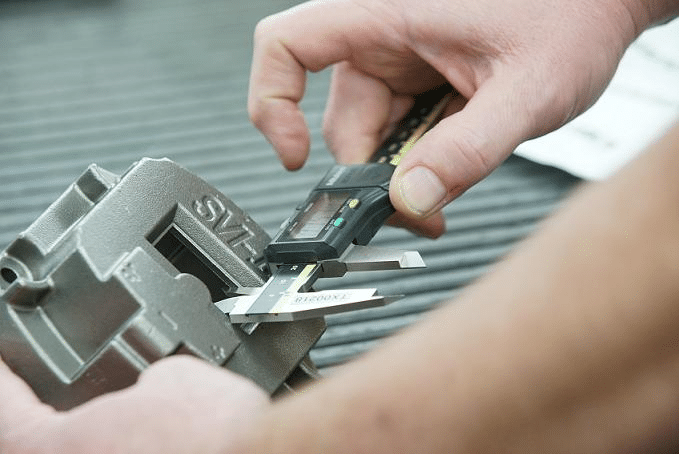
Coordinate Measuring Machines verify dimensions to ±0.005mm accuracy. Statistical process control tracks consistency across wide range of industries. Automotive Tier 1 suppliers inspect 100% of safety-critical features per IATF 16949 requirements.
X-ray inspection reveals internal porosity non-destructively. Aerospace die cast components undergo complete scanning. Medical applications sample at 10-15% rates. Leak testing validates pressure-tight requirements using helium trace methods.
Material Certification Standards
Chemical analysis confirms casting alloys meet specifications. Spectrographic testing verifies composition for aluminum and zinc. Certification documents accompany shipments proving material traceability through the supply chain.
Mechanical testing validates strength properties. Tensile testing on sample die cast part units ensures consistency. Hardness testing confirms heat treatment effectiveness for aluminum die casting alloys requiring thermal processing.
Environmental Considerations in Die Casting
Material efficiency minimizes waste. The die casting process uses 95-98% of metal versus cnc machining’s 30-60% efficiency. Runner systems and flash become scrap—all recyclable through closed-loop systems.
Aluminum and zinc recycle infinitely without property degradation. Many die casting manufacturing facilities operate in-house recycling. Metal solidifies quickly in ingot molds for immediate reuse, reducing supply chain complexity.
Energy Efficiency Benefits
High-volume production amortizes energy costs. General Motors reports 65% energy savings per component versus machined alternatives. Die casting machines ranging from 250 to 2,800 tons run continuously—maximizing efficiency versus batch processes.
Modern cold chamber casting systems recover waste heat. This preheats aluminum parts and reduces melting energy 20%. Combined with repeatable quality requiring minimal rework, the metal casting process delivers strong environmental performance.
About Yicen Precision Die Casting Capabilities
Yicen Precision operates ISO 9001:2015 certified facilities serving automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturers since 2007. Our die casting capabilities include 8 machines ranging from 400 to 2,800 tons producing aluminum parts, zinc die cast components, and magnesium castings.
We offers custom solutions with in-house precision machining, powder coating, and CMM inspection. Our engineering team provides detailed DFM analysis ensuring die castings that meet exact specifications. Contact us to learn how our die casting services support your project needs.
Recent Project Success
In 2024, we produced 28,000 aluminum heat sink housings for a leading electronics manufacturer. Challenge: achieve 0.8mm walls with ±0.15mm tolerance maintaining 99.5%+ yield. Solution: vacuum-assisted high pressure die casting with optimized gating. Result: client reduced assembly costs 38% while improving thermal performance 22%.
Our zinc die casting capabilities serve medical device companies requiring biocompatible materials. Precision components ship with full material certification and dimensional reports. Learn more about die casting possibilities for your application.
Conclusion
Die casting offers efficient production for medium-to-high volumes using aluminum, zinc, or magnesium. The process excels at complex metal parts requiring tight tolerances and excellent surface finish. Success demands proper material selection, experienced die casting manufacturer partnership, and volume exceeding 1,500 units annually. Projects requiring high-precision metal components with repeatable quality typically achieve optimal value through certified die casting solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What minimum volume justifies die casting costs?
Break-even occurs at 1,500-2,000 units annually. Tooling costs $15,000-$150,000 which smaller volumes can’t support. Lower quantities work better with cnc machining or investment casting alternatives.
How long does die casting tooling last?
Aluminum casting dies average 180,000-280,000 cycles. Zinc die casting extends to 450,000+ shots. Copper reduces life to 120,000 cycles due to higher temperatures damaging the tool faster than other casting alloys.
Can threads be cast directly into parts?
No—threads require secondary operations after the die casting process. Use tapping, thread milling, or threaded inserts on cast components. This adds $0.40-$1.80 per location to manufacturing costs.
What metals work with die casting?
Aluminum die casting alloys (65% market), zinc (25%), magnesium (8%), and copper (2%) work reliably. Steel and iron exceed temperature limits—dies fail rapidly with these materials requiring alternative casting methods.
What’s typical production timeline for die cast parts?
Simple dies require 4-8 weeks. Complex multi-cavity tools need 8-12 weeks. Add 1-2 weeks for first article sampling. Total time from approved design to production: 8-14 weeks through quality die casting service providers.
References and Citations
- North American Die Casting Association (NADCA). (2024). “Die Casting Industry Statistics and Production Data Report.” https://www.diecasting.org/industry-data – Comprehensive annual compilation covering production volumes, material segmentation, tolerance standards, and quality benchmarks from 300+ certified member facilities across the United States.
- Smithers Rapra Technology. (2024). “Global Die Casting Market Analysis and Forecast 2024-2030.” https://www.smithers.com/resources/2024/die-casting-market-report – Market research analyzing aluminum die casting, zinc die casting, and magnesium production trends, automotive applications, and supply chain dynamics.
- SAE International Standards Committee. (2023). “AMS-QQ-A-596: Aluminum Alloy Die Castings Specification.” https://www.sae.org/standards/content/ams-qq-a-596 – Technical specification defining aerospace-grade die casting requirements, tolerance classes, material certification, and inspection protocols for high-precision metal components.
- ASM International Handbook Committee. (2024). “ASM Handbook Volume 15: Casting Processes and Technologies.” https://www.asminternational.org/home/-/journal_content/56/10192/15261482 – Comprehensive technical reference covering die casting process parameters, casting alloys properties, defect analysis, quality control methodologies, and surface finish specifications for manufacturing engineers.