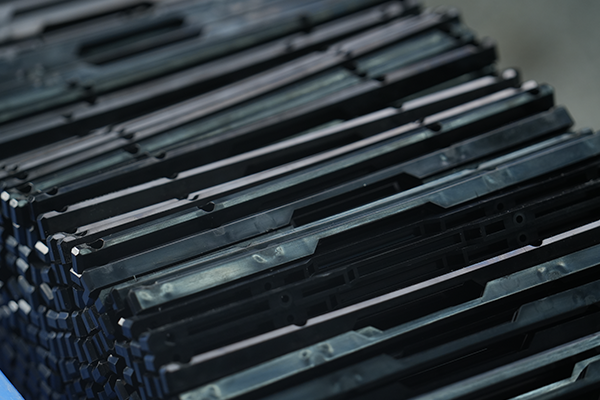
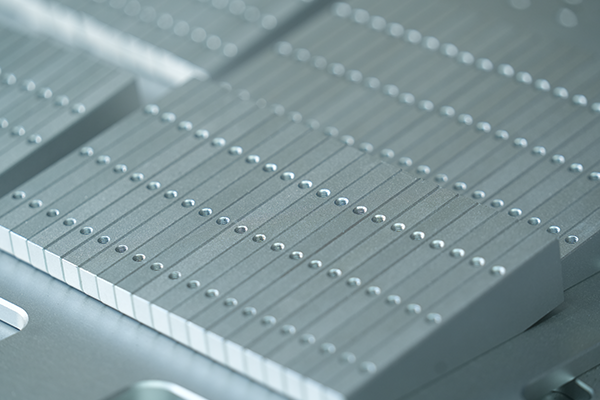
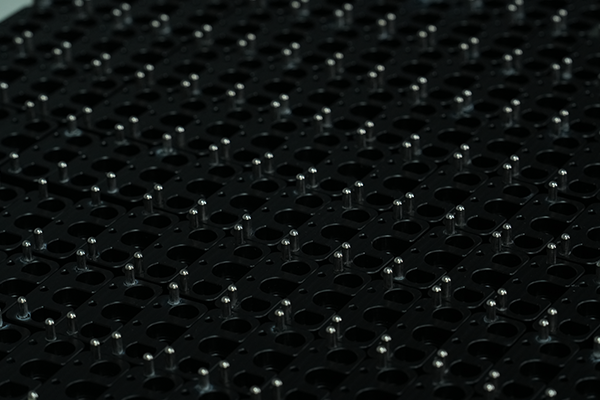
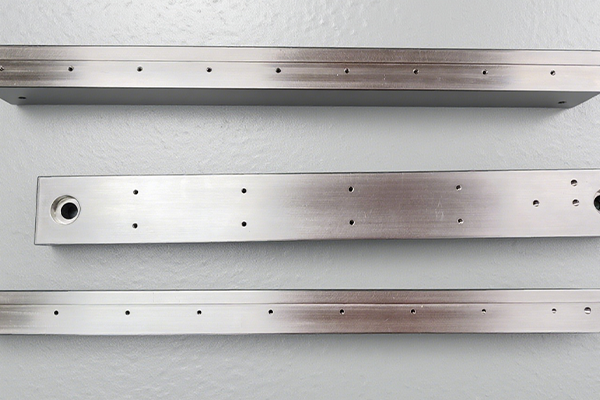
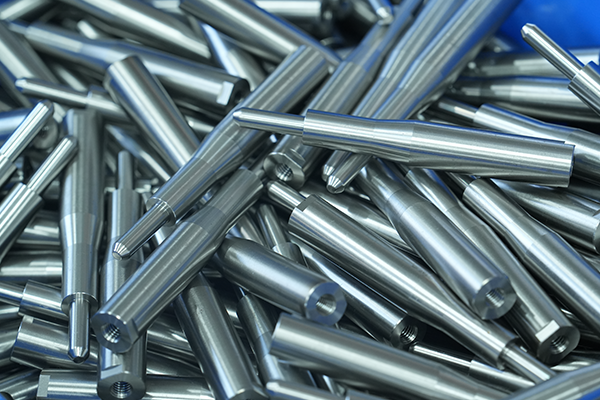
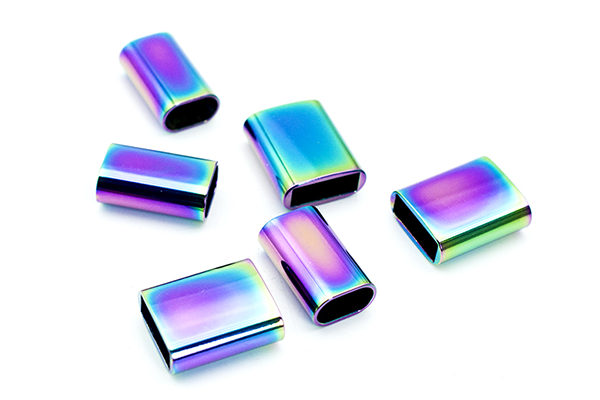
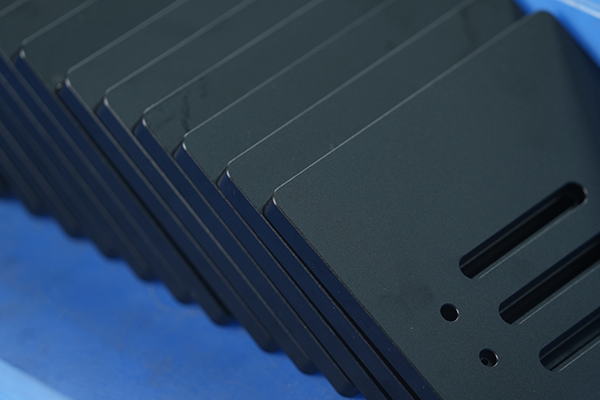
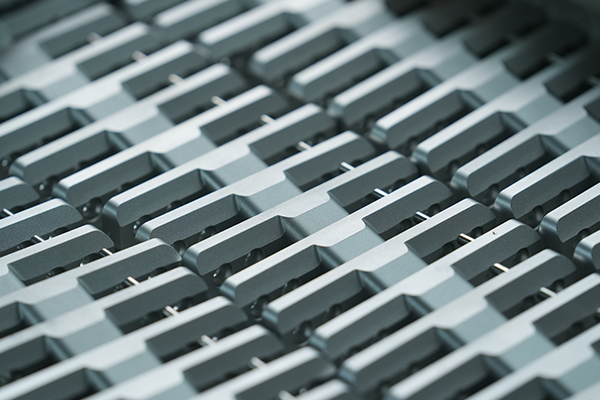
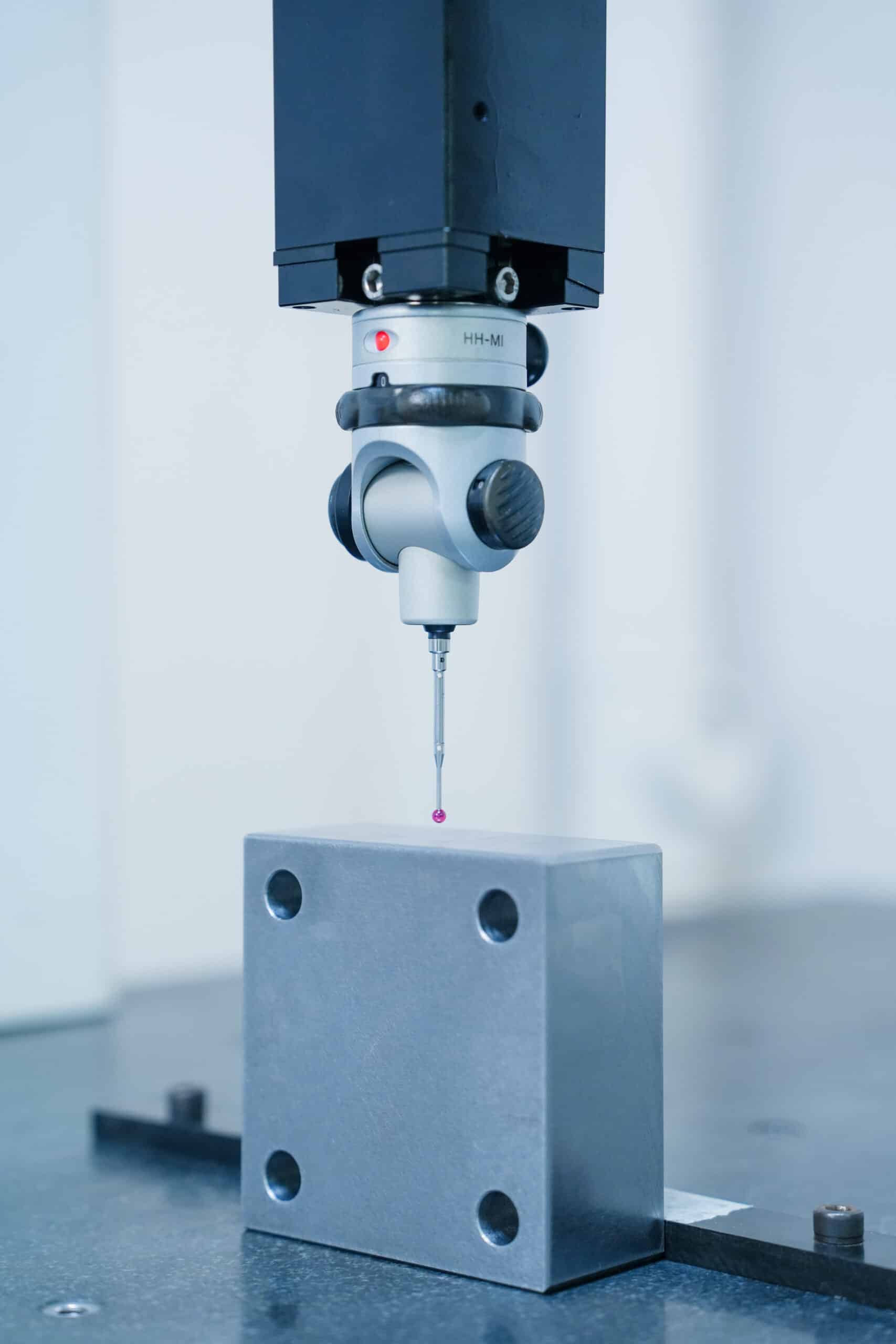
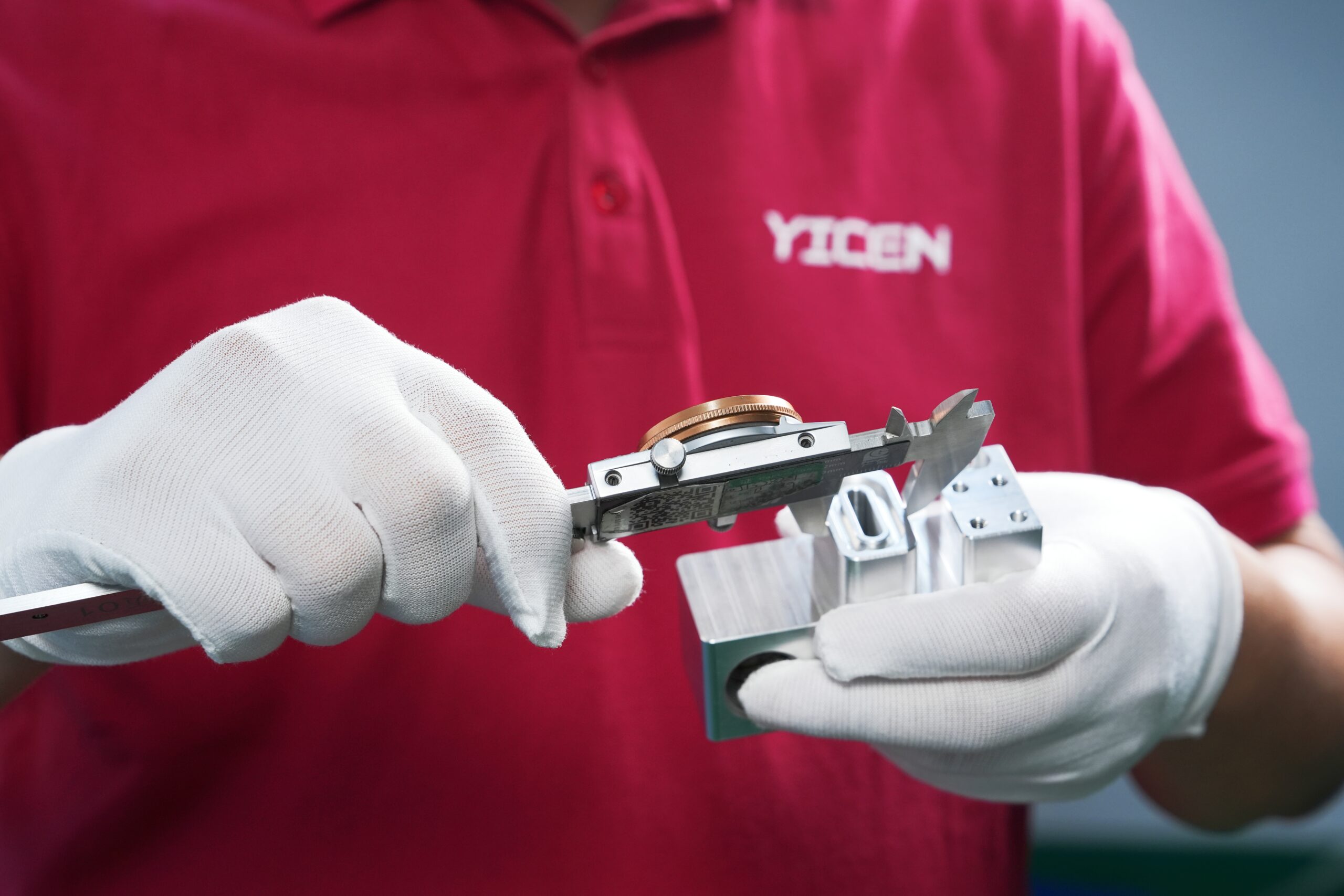
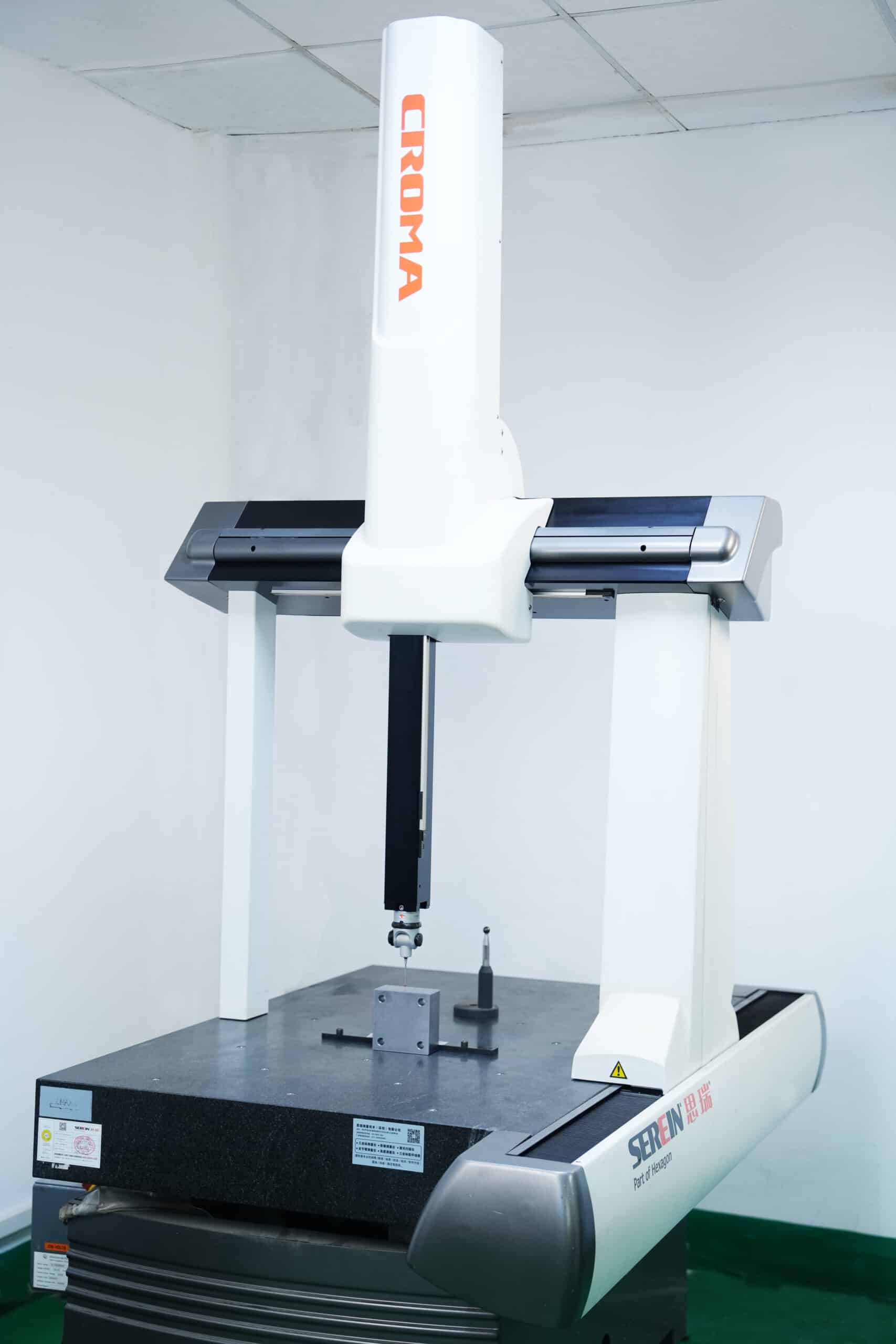
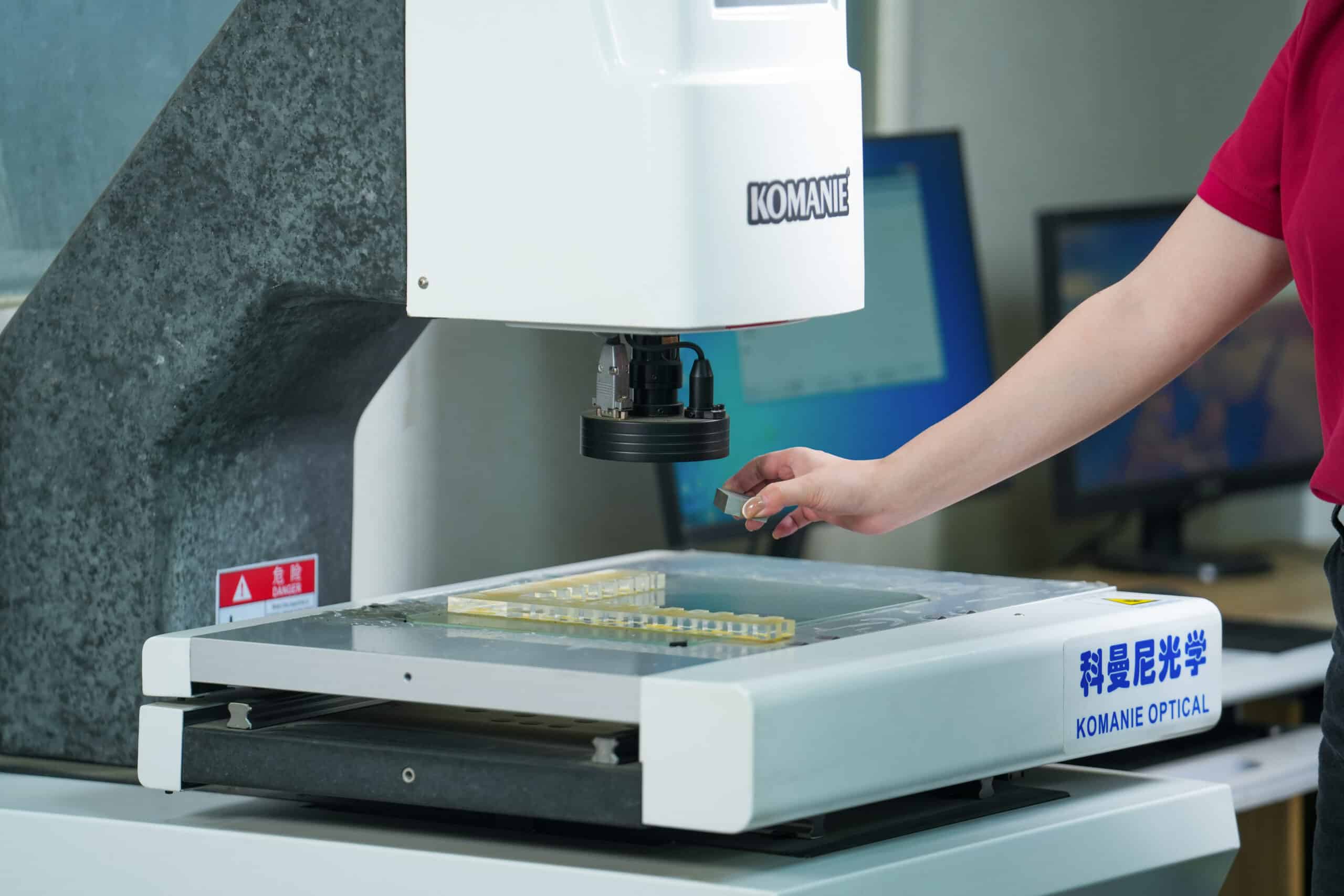
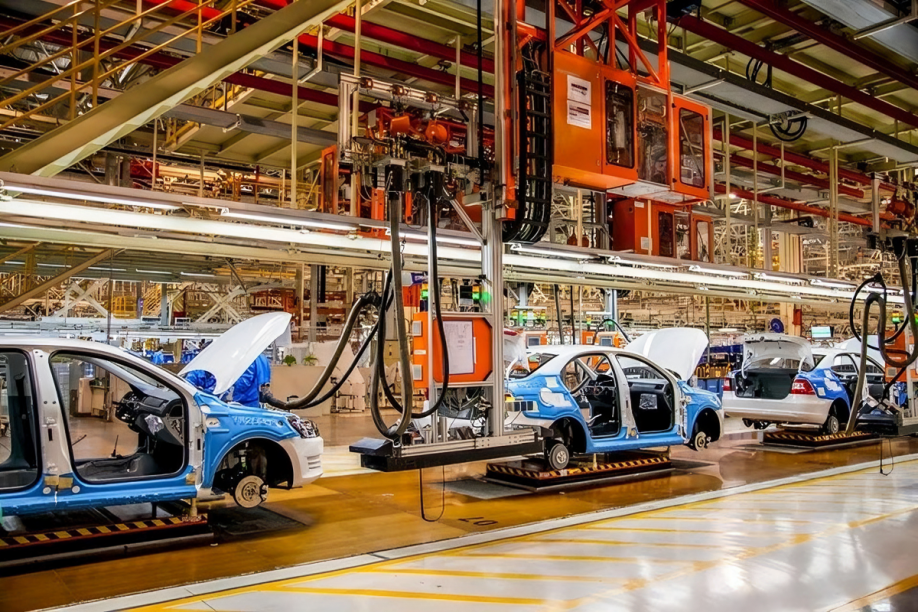
FDM is a cost-effective 3D printing method that offers fast production times, no tooling costs, and the ability to use durable materials like ABS et Nylon. It’s best for low-volume production and prototyping, while other technologies like ALS ou SLS may be better suited for high-detail or high-precision parts.