What is Fool-Proofing in Jigs & Fixtures?
Definition of Fool-Proofing (Poka-Yoke) in Manufacturing
Fool-proofing, also known as Poka-Yoke, is a design methodology aimed at preventing errors before they occur. In the context of 治具と固定具、 fool-proofing involves incorporating features that make it impossible for the operator to make mistakes when setting up, using, or assembling the workpiece. By designing jigs and fixtures to eliminate human error, fool-proofing ensures high-quality, consistent results in manufacturing processes.
Why it is Used in Tooling, Workholding, and Assembly Fixtures
Fool-proofing is particularly crucial in tooling, workholdingそして assembly fixtures where precise positioning and orientation are vital. In these applications, even a small mistake can lead to defective parts, increased scrap rates, and costly rework. By implementing fool-proofing features, designers ensure that fixtures and jigs guide the operator toward the correct setup, reducing the likelihood of errors such as misloading or misorientation.
Role in Preventing Operator Errors, Misloads, Orientation Mistakes
Fool-proofing plays a significant role in preventing common operator errors, such as misloads そして orientation mistakes. These errors can happen when parts are incorrectly placed or positioned, leading to improper 加工, assembly, or welding. Fool-proofing mechanisms, such as asymmetrical locators または sensor-based systems, guide the operator, ensuring that the part is loaded in the correct orientation and position every time.
Difference Between Fool-Proofing vs. Quality Inspection
一方 quality inspection is used to identify and correct defects after they have occurred, fool-proofing focuses on preventing defects during the initial setup or operation. Fool-proofing integrates design features that automatically prevent errors, making it much more proactive than quality inspection, which only corrects errors after they occur.
Why Fool-Proofing Is Essential in Modern Manufacturing
Rise of Automation + Human-Machine Interaction
The integration of automation and human-machine interaction (HMI) has transformed modern manufacturing. While 機械 can be highly accurate, human operators still interact with the systems. Fool-proofing designs mitigate the risk of human error, ensuring that the interaction between operators and 機械 is smooth and error-free, especially in high-speed, high-precision environments.
Need for Consistent, Error-Free Production
In industries like automotive, aerospace, and precision 加工, consistent, error-free production is non-negotiable. Even the smallest deviation can lead to catastrophic failures, significant costs, and safety risks. Fool-proofing ensures that production processes remain consistent そして predictable, leading to higher product quality and lower defect rates.
Cost of Errors in Automotive, Aerospace, and Precision Machining
について cost of errors in fields like automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and precision 加工 can be astronomical. A single faulty component could lead to recalls, catastrophic system failures, or safety hazards. Fool-proofing is a proactive approach that helps reduce these risks, preventing costly mistakes before they happen.
Impact on Takt Time, Quality Metrics, First-Pass Yield (FPY)
Fool-proofing has a direct impact on takt time, quality metricsそして first-pass yield (FPY). By preventing errors, it reduces the need for rework and reassembly, improving overall cycle times and efficiency. High first-pass yield ensures that a greater proportion of parts are produced correctly the first time, reducing scrap and improving throughput.
Common Mistakes Prevented by Fool-Proof Design
Workpiece Misalignment
Fool-proof designs help prevent workpieces from being misaligned in the fixture, ensuring that they are positioned correctly for the intended operation. Locating pins または step locators are common fool-proofing mechanisms used to prevent misalignment during 加工.
Wrong-Part Loading
Inaccurate or wrong-part loading is a common issue that can cause significant delays or quality problems. Fool-proof designs, such as asymmetrical locators または keyed blocks, ensure that only the correct part can be loaded into the fixture in the correct orientation.
Incorrect Orientation (R/L, Top/Bottom)
Fool-proofing ensures that the workpiece is loaded in the correct orientation, whether it’s right/left (R/L) または top/bottom. Visual guides, sensor-based fool-proofingそして orientation-specific slots prevent incorrect part orientation.
Missing Components in Assembly
In assembly fixtures, missing components can lead to incomplete or non-functional assemblies. Fool-proofing ensures that all necessary parts are included in the fixture setup before assembly begins, often using sensor-based validation または physical blockers that prevent the assembly from starting unless all components are present.
Improper Clamping Sequence
について clamping sequence is crucial in ensuring that the workpiece remains stable and secure during 加工. Fool-proof designs often include sequence-controlled clamps that ensure the correct clamping order, preventing potential damage or misalignment during operations.
Tool Collision and Robotic Path Errors
In automated environments, improper tool collision または robotic path errors can be catastrophic. Fool-proofing designs use path simulation, proximity sensorsそして collision detection to ensure that the tool or robot doesn’t interfere with other parts of the system.
Types of Fool-Proofing Used in Jigs & Fixtures
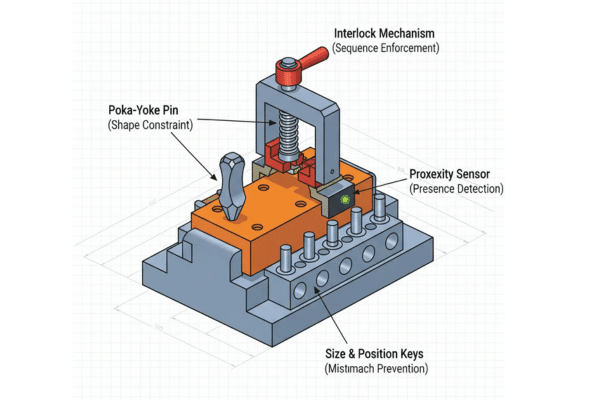
Mechanical Fool-Proofing
- Dowels: Ensure the correct positioning of parts by preventing rotation or movement.
- Locating Pins: Pin systems prevent parts from being loaded incorrectly by restricting movement to the correct alignment.
- Keyed Blocks: Only allow correct part orientation and positioning, preventing errors.
- Step Locators: Ensure that parts are seated at the correct level, avoiding misalignment.
- Interference Blocks: Prevent the closure of the jig if the part is not properly loaded.
Visual Fool-Proofing
- Labels: Clear, legible labels help operators quickly understand how parts should be oriented or loaded.
- Color-Coded Features: Color coding guides the operator to place components in specific slots or positions, preventing errors.
- Visual Orientation Guides: These guides provide easy-to-follow markings or illustrations that show the correct part placement.
Sensor-Based Fool-Proofing
- Proximity Sensors: Ensure that the part is properly positioned before the 機械 starts the operation.
- Limit Switches: Prevent the system from engaging if the workpiece is not correctly positioned or clamped.
- Laser Sensors: Detect the exact position of the workpiece or tool to ensure correct placement.
- RFID/Barcode Validation: Ensures the right part is loaded by scanning embedded tags or barcodes, providing validation before production begins.
Error-Proof Clamping Systems
- Sequence-Controlled Clamps: These systems ensure that clamps engage in the correct order, preventing errors during setup and operation.
- Pneumatic/Hydraulic Interlock: Interlocking systems that only allow operations to proceed if all clamps are correctly engaged, reducing errors in multi-clamp setups.
Digital Fool-Proofing (Industry 4.0)
- PLC Logic: Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) can be programmed to ensure fool-proof operations by controlling the sequence of operations.
- Fixture-Mounted Smart Sensors: Smart sensors embedded in the fixture can detect part presence and orientation, ensuring correct alignment before proceeding.
- Error Detection in Robotic Assembly: Automated systems can use digital error-checking to prevent misloads or incorrect assembly steps.
Fool-Proofing in BIW (Body-in-White) Fixtures
Why BIW is Highly Sensitive to Errors
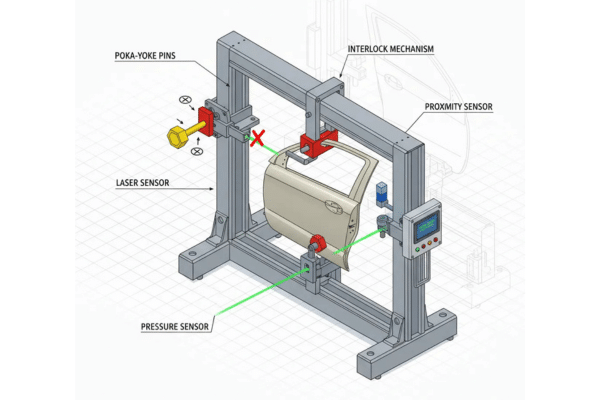
In automotive manufacturing, Body-in-White (BIW) fixtures are particularly sensitive to errors due to the need for precision in assembly. Even small errors in part orientation or alignment can lead to catastrophic issues during the final assembly stage or even after the car has been produced.
How Fool-Proofing Improves Weld Quality & Dimensional Accuracy
Fool-proofing ensures that parts are loaded correctly in the BIW fixture. Geo fixture locator fool-proofing ensures that parts align with extreme precision, which improves weld quality そして dimensional accuracy, reducing the chances of structural weaknesses.
例
- R/L Discrimination Pins: Pins designed to prevent incorrect part orientation in the fixture.
- Geo Fixture Locator Fool-Proofing: Locator features that ensure parts are positioned correctly, preventing misalignment during welding.
- Mylar Assembly Pin Blockers: Blockers that ensure the part cannot be loaded incorrectly, preventing orientation mistakes.
- Sensor Validation Before Weld Gun Cycle: Sensors that ensure proper alignment and placement before welding begins, reducing errors in the final product.
Fool-Proofing in Aerospace Assembly Jigs
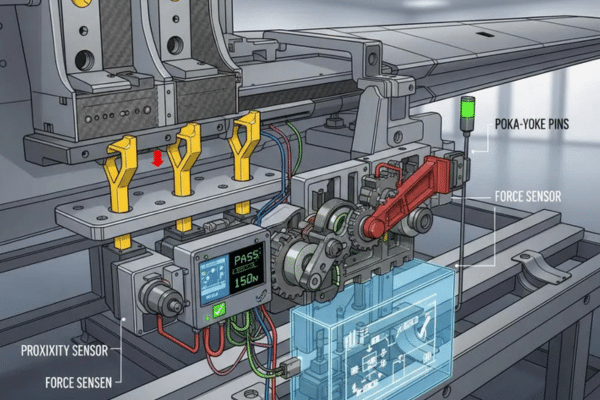
Precision and Safety Requirements in Aerospace
In aerospace manufacturing, precision and safety are paramount. Fool-proofing ensures that parts are aligned そして machined correctly to meet the high standards required for safety and performance.
Prevention of FOD (Foreign Object Damage)
Fool-proofing mechanisms in aerospace assembly jigs help prevent FOD (Foreign Object Damage) by ensuring that no tools or components are left in the assembly before the fixture is removed.
Fool-Proofing in Wing, Fuselage, and Composite Lay-Up Fixtures
Fool-proofing in wing, fuselageそして composite lay-up fixtures is crucial in ensuring that parts are properly aligned and fixed in place before assembly begins. These features prevent errors that can affect the structural integrity of the aircraft.
Sensor Integration for Robotic Drilling Fixtures
Advanced fool-proofing using sensor integration ensures that robotic drilling fixtures operate with high accuracy, reducing the risk of misalignment そして tooling errors.
How to Design Fool-Proof Jigs & Fixtures (Engineering Checklist)
1. Understand Operator Behavior and Workflow
Designers should analyze the typical workflow and behavior of operators to anticipate potential errors and design fixtures and jigs that account for common mistakes.
2. Identify Potential Human + Machine Failure Points
Assess all points where human error or 機械 malfunction could occur and incorporate fool-proofing features to eliminate these risks.
3. Ensure Asymmetrical Positioning Features
Asymmetrical features, such as asymmetrical locators または keyed blocks, prevent parts from being loaded in the wrong orientation.
4. Validate Orientation with Pins/Blocks
Locating pins そして step blocks should be used to confirm the correct orientation of the workpiece in the fixture, preventing improper assembly.
5. Add Interlocks for Safety and Sequence
Interlocking clamping systems そして sequence-controlled mechanisms ensure that parts are clamped in the correct order and at the right time.
6. Test with Multiple Operators
Before finalizing a design, test it with multiple operators to ensure that the fool-proof features work as intended in various scenarios.
7. Run FMEA for Fool-Proofing Effectiveness
Perform Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to evaluate the potential for failure in the fool-proofing system and identify areas for improvement.
Benefits of Fool-Proofing in Jig & Fixture Design
- Zero Rework and Scrap Reduction: Prevents errors that lead to rework or scrap.
- Maximum Repeatability: Ensures consistent part quality with minimal variation.
- Reduced Operator Skill Dependency: Reduces the need for highly skilled labor by guiding operators through the correct setup.
- Consistent Assembly Accuracy: Increases part accuracy and precision during assembly.
- Faster Cycle Time: Minimizes setup time by eliminating the need for error correction.
- Enhanced Machine & Operator Safety: Reduces the risk of accidents by ensuring that fixtures are safely secured and operate as intended.
Real-World Examples
Automotive BIW
- Door Inner Panel Fixture Fool-Proofing: Locators and blockers ensure the correct part and orientation are used during assembly.
- Chassis Sub-Assembly Fixture Orientation Blocks: Blocks ensure that parts are oriented correctly, preventing misalignment.
航空宇宙
- Composite Lay-Up Jigs: Fool-proof features ensure that 材料 are correctly layered and oriented for strength and safety.
- Precision Drilling Fixtures: Sensors and guides ensure correct drilling positions, minimizing errors.
CNC加工
- Wrong-Part Prevention: Asymmetrical locators and RFID tags ensure that only the correct parts are loaded into the fixture.
- One-Way Loading Nests: Nests are designed to allow parts to be loaded in one orientation only, preventing misloads.
結論
Fool-proofing is an essential strategy in jig and fixture design, ensuring high-quality, error-free production. By integrating fool-proofing features, manufacturers can reduce rework, improve consistencyそして enhance safety. Incorporating fool-proofing from the design stage is crucial for creating efficient and reliable manufacturing processes.
よくあるご質問
What does fool-proofing mean in jig and fixture design?
Fool-proofing in jig and fixture design means creating a setup that prevents incorrect loading, orientation, or operation, even if the operator makes a mistake. The fixture physically allows only the correct part position and sequence. This is achieved through asymmetric locating, poka-yoke features, and controlled clamping logic. The goal is to eliminate human error rather than rely on training alone.
Why is fool-proofing critical in high-volume production?
In high-volume production, even a small error rate quickly turns into large scrap quantities and rework costs. Fool-proofed fixtures ensure that every part is loaded the same way, every time, regardless of operator skill or shift changes. This consistency protects cycle time, part quality, and downstream assembly. It also reduces inspection load and production stoppages.
How do fool-proof jigs and fixtures reduce quality issues?
Fool-proof fixtures eliminate common quality problems such as incorrect datum referencing, flipped parts, misalignment, and partial clamping. By enforcing correct locating and clamping sequences, they ensure machining happens relative to the intended reference surfaces. This directly improves dimensional accuracy, repeatability, and surface finish consistency. Many quality escapes originate from fixtures that allow multiple incorrect setups.
What are common fool-proofing features used in jigs and fixtures?
Common fool-proofing features include asymmetric locating pins, key-and-slot designs, part-specific nests, guided clamp sequencing, and physical stops that block incorrect loading. Some fixtures also use sensors or mechanical interlocks to prevent machine start unless the part is properly seated. The simplest mechanical fool-proofing solutions are often the most reliable and maintenance-free.
Is fool-proofing still necessary when using CNC machines?
Yes, fool-proofing is even more important in CNC machining. CNC machines repeat mistakes perfectly and rapidly if a part is loaded incorrectly. Unlike manual machining, the operator cannot compensate mid-cycle. Fool-proof fixtures act as a final safety layer between human interaction and automated cutting, protecting both the part and the machine from costly errors.