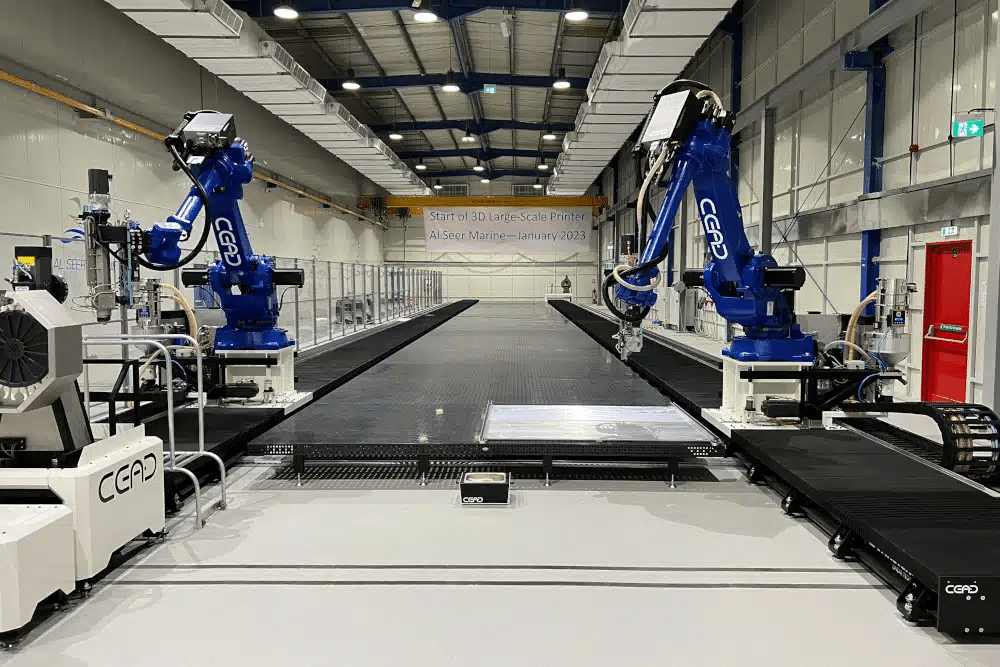
Manufacturing oversized components has always presented challenges. Traditional methods require extensive tooling, long lead times, and often result in parts that need assembly. Large 3D printing services change this equation by producing sizable components in single builds.
The technology continues advancing rapidly. According to IMARC Group, the global 3D printing market reached $28.5 billion in 2024 and projected growth to $125.9 billion by 2033. Industrial applications dominate this expansion, with large format 3D printers capturing significant adoption across aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing sectors.
This guide explores how businesses integrate large-scale additive manufacturing with traditional CNC加工サービス capabilities for optimal results.
Understanding Large Format 3D Printing Technology
Large format 3D printers differ substantially from desktop units. While standard machines handle objects around 12 inches cubed, industrial systems produce parts measuring several feet in each dimension. Build volumes commonly range from 36″ x 24″ x 36″ up to 10 feet for specialized equipment.
The technology serves distinct purposes. Some manufacturers use it for rapid prototyping. Others produce end-use parts that traditional machining cannot economically create. Many companies combine large 3D printing services と CNC加工サービス operations to leverage both technologies’ strengths.
Market data from Precedence Research shows industrial 3D printers held 77% of market share in 2024. This dominance reflects their ability to handle demanding applications requiring precision and material variety.
Primary Technologies in Large Scale Printing
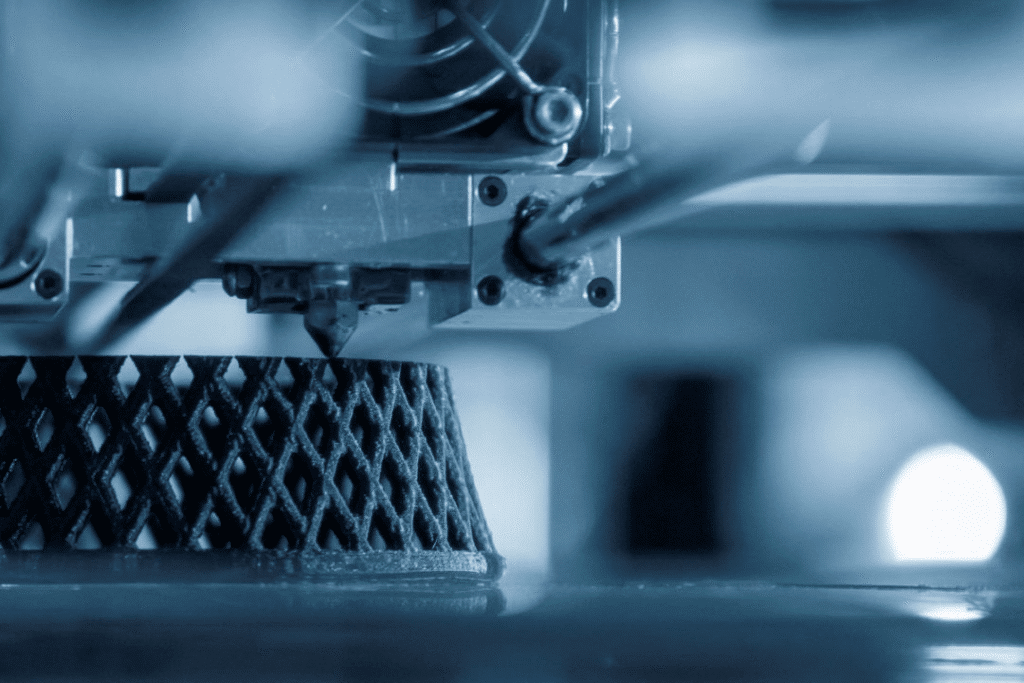
Different processes suit different needs. Here’s what actually works in production environments.
溶融堆積モデリング(FDM)
多重伝送装置 remains the workhorse for plastic parts. The process melts thermoplastic filament layer by layer. Maximum build sizes reach 36″ x 24″ x 36″ in many industrial systems. Materials include ABS, nylon, polycarbonateそして carbon fiber composites.
Companies appreciate FDM because it’s straightforward and cost-effective. Parts emerge ready for functional testing without elaborate post-processing. When combined with CNC service finishing, FDM parts achieve surprisingly tight tolerances.
ステレオリソグラフィー(SLA)
エスエルエー uses UV lasers to cure liquid resin. Stratasys launched the Neo800+ in March 2025, offering 800 x 800 x 600 mm build volume. The system achieves print speeds 50% faster than previous models while maintaining accuracy for aerospace and automotive applications.
Surface finish quality makes SLA popular for visual prototypes and master patterns. The technology produces parts that look production-ready straight from the machine.
選択的レーザー焼結(SLS)
SLS fuses powder without support structures. This advantage enables complex geometries impossible with other methods. Parts emerge fully supported by surrounding powder during the build process.
No support removal means reduced labor costs and faster turnaround. Internal channels, lattice structures, and interlocking assemblies print without the constraints other technologies face.
ダイレクトメタルレーザー焼結(DMLS)
DMLS creates metal components for high-performance applications. The US Air Force awarded 3D Systems a $7.65 million contract in August 2025 for the GEN-IIDMP-1000, a large format 3D printer specifically designed for military applications.
Metal printing opens possibilities traditional machining cannot touch. Complex cooling channels inside tooling, lightweight aerospace brackets with organic shapes, and patient-specific medical implants all leverage DMLS capabilities.
Binder Jetting
Binder Jetting offers the largest build volumes, reaching 72″ x 48″ x 24″ in some systems. The technology works well for sand casting molds and prototypes requiring massive size. Speed represents another advantage—multiple parts print simultaneously across the build platform.
Industry Applications Driving Growth
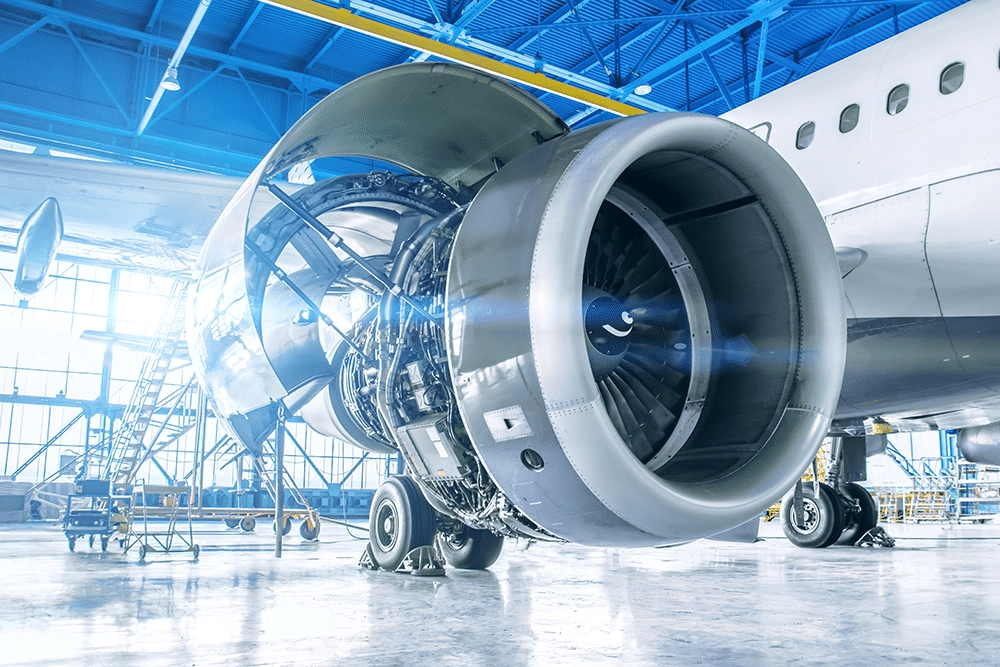
Real-world adoption tells the story better than predictions. Let’s look at where large 3D printing services actually make business sense.
Aerospace Manufacturing
について 航空宇宙 3D printing market totaled $3.53 billion in 2024, according to Fortune Business Insights. Projections show growth to $14.53 billion by 2032.
SpaceX established an $8 million licensing agreement with Velo3D in September 2024. The partnership focuses on metal additive manufacturing for rocket components. SpaceX already prints the SuperDraco engine entirely through additive processes—something unthinkable a decade ago.
Weight reduction drives adoption. Large 3D printing services enable part consolidation that cuts component weight 40-60% compared to traditional manufacturing. GE Aerospace’s LEAP fuel nozzle merges 20 separate pieces into one printed part. That consolidation means fewer potential failure points and simpler assembly.
自動車部門
Automotive manufacturers leverage large format 3D printers for both prototyping and production tooling. The technology accelerates development cycles while reducing costs—two priorities that rarely align in manufacturing.
Fortune Business Insights reports the automotive segment held 25% of the industrial 3D printing market in 2024. Custom tooling, jigs, fixtures, and low-volume production parts represent primary applications.
Integration with CNC service capabilities proves valuable here. Printed parts often receive CNC machining for critical mounting surfaces and tight-tolerance features. This hybrid approach delivers results faster and cheaper than either technology alone.
Medical and Healthcare
Healthcare applications focus on patient-specific devices and surgical planning models. Anatomical models printed at full scale help surgeons prepare for complex procedures, reducing operating time.
The medical segment shows robust growth projections at 25.33% CAGR through 2030, per Markets and Markets data. Customization drives this growth—every patient’s anatomy differs, making mass production irrelevant for many applications.
Materials for Large Format Production
Material choice determines whether a part succeeds or fails. Engineers need to match material properties to application requirements.
| Material Category | Common Types | 代表的なアプリケーション | Price Range per kg |
| エンジニアリングプラスチック | ABS, Nylon, PC, PETG | Functional prototypes, tooling | $50-$200 |
| High-Performance Polymers | PEEK, Ultem | Aerospace, medical devices | $300-$600 |
| 金属合金 | Aluminum, Titanium, Stainless Steel | Aerospace, automotive components | $200-$500 |
| 複合材料 | Carbon Fiber reinforced | Structural parts, high-strength applications | $100-$300 |
Metal materials dominate aerospace applications. Mordor Intelligence reports metal alloys captured 60.5% of aerospace 3D printing revenue in 2024. チタン remains essential for high-temperature applications like combustor liners and turbine blades. The material’s strength-to-weight ratio outperforms alternatives, justifying higher costs.
When Large Format Printing Makes Sense
Not every large part belongs in an additive machine. Understanding the boundaries saves time and money.
Good candidates for large 3D printing services:
- Complex geometries with internal features
- Low to medium volume production (1-500 units)
- Parts requiring rapid iteration during development
- Components where weight reduction justifies higher material costs
- Designs that consolidate multiple assemblies
Better suited for traditional manufacturing:
- Simple geometric shapes
- High volume production (10,000+ units)
- Parts requiring extremely tight tolerances throughout (under ±0.1mm)
- Applications where material cost drives total economics
- Designs already optimized for conventional machining
Sometimes the answer involves both. Print the complex internal structure, then machine the precision mounting surfaces. 易岑精密の integrated capabilities support exactly this workflow.
Common Mistakes That Cost Money
Experience reveals patterns in what goes wrong. Avoiding these issues saves both time and budget.
Underestimating Post-Processing Requirements
Raw printed parts rarely meet final specifications directly. Support removal takes time. Surface smoothing adds labor. Post-processing typically adds 20-40% to base printing costs—yet many budget estimates ignore this reality.
Plan for finishing from the start. Include sanding, tumbling, painting, or CNC加工サービス in both timeline and cost projections. Parts that look complete in the slicer software still need human attention afterward.
Ignoring Print Orientation Effects
Orientation affects everything. Strength can vary 30-50% depending on how layers align relative to loading direction. Surface finish differs dramatically between vertical and horizontal faces. Support structures leave marks that require removal.
Work with your service provider on orientation strategy before committing to production. Sometimes rotating a part 45 degrees eliminates support structures entirely, saving hours of labor and improving final quality.
Selecting Materials Based on Price Alone
Cheapest material rarely delivers best value. A part printed in standard ABS might cost $300, while the same part in carbon fiber nylon runs $800. Yet if the ABS part fails in service and requires redesign, those savings evaporate quickly.
Match material properties to actual application requirements. Thermal resistance, chemical compatibility, UV stability, and mechanical strength all matter depending on use case. Spending more upfront often costs less overall.
Cost Considerations
Large 3D printing services pricing depends on multiple factors that interact in non-obvious ways.
A typical 12″ x 12″ x 12″ FDM part in engineering plastic runs $300-$500. The same size in DMLS aluminum costs $2,500-$4,000. Post-processing adds 20-40% to base printing costs. These numbers vary based on geometry complexity, material choice, and required finish quality.
Combining technologies often reduces total costs. Printing a near-net shape part then CNC加工 critical features can save 30-60% versus full CNC fabrication from solid stock. The math works because you eliminate massive material waste while maintaining precision where it matters.
Volume economics shift the equation. Single prototypes favor additive manufacturing. Production runs exceeding 1,000 units often justify tooling investment for traditional processes. The crossover point depends on part complexity and design requirements.
Integrating with CNC Machining Services
Hybrid manufacturing leverages both additive and subtractive processes. Real production environments increasingly blend technologies rather than choosing one exclusively.
When to combine technologies:
- Complex internal geometries requiring tight-tolerance external features
- Large parts needing precise mounting surfaces
- Reducing material waste on oversized components
- Achieving surface finishes finer than printing produces
The process typically involves printing parts 1-2mm oversized, then CNC加工 final dimensions and critical surfaces. Companies report 40-60% cost savings versus full CNC machining for large components. That’s not theoretical—those numbers come from actual production data.
易岑精密の integrated capabilities support this hybrid approach. CNC加工サービス options complement additive manufacturing for complete manufacturing solutions. One vendor, one timeline, consistent quality management across processes.
Design Guidelines for Success
Proper design prevents costly failures. These aren’t theoretical recommendations—they’re lessons learned from thousands of builds.
Wall Thickness Parameters
Maintain 1.0-1.5mm minimum for FDM plastics. Metal parts require 0.4-0.8mm minimums. Avoid walls exceeding 10mm to prevent warping—thick sections cool unevenly, inducing internal stresses that manifest as dimensional problems.
Uniform wall thickness works better than varying profiles. When thickness changes are necessary, transition gradually over several centimeters rather than creating sharp steps.
サポート体制戦略
FDM and SLA need supports for overhangs beyond 45 degrees. Orient parts strategically to minimize support material and reduce post-processing time. Every support contact point leaves a mark requiring cleanup.
Design self-supporting features where possible. Chamfers replace vertical walls. Gradual angles avoid support entirely. These adjustments during CAD work save hours during finishing.
Tolerance Expectations
Expect ±0.5mm for FDM, ±0.3mm for SLS, ±0.2mm for SLAそして ±0.1mm for DMLS. CNC加工サービス post-processing tightens tolerances to ±0.05mm or better where specifications demand precision.
Apply tight tolerances selectively. Machining every surface drives costs up unnecessarily. Identify critical dimensions requiring precision, then specify economical tolerances elsewhere.
Strength Considerations
Print orientation affects strength by 30-50%. Parts loaded perpendicular to layer lines show reduced strength. Design accordingly or add ribbing for reinforcement.
Solid infill increases strength but also weight and cost. Strategic infill placement—dense in stressed areas, sparse elsewhere—optimizes the strength-to-weight ratio while controlling material consumption.
Material Selection Deep Dive
Choosing the right material requires understanding how properties translate to real-world performance.
Engineering plastics ような ABSとナイロン handle most prototyping needs. They’re forgiving during printing, reasonably priced, and deliver adequate mechanical properties for testing. PETG offers better chemical resistance when parts contact solvents or oils.
High-performance polymers enter when conditions get extreme. 覗き見 withstands continuous temperatures up to 260°C and resists nearly every chemical. Medical applications favor it for biocompatibility. Ultem brings similar performance with added flame resistance—critical for aerospace interiors.
Metal alloys dominate when strength, stiffness, or thermal properties exceed polymer capabilities. アルミニウム合金 deliver excellent strength-to-weight ratios with good thermal conductivity. チタン costs more but offers superior strength and corrosion resistance. ステンレス balances cost, strength, and environmental resistance.
複合材料 blend characteristics. Carbon fiber reinforced nylon delivers steel-like stiffness at plastic weight. These materials typically cost $100-300 per kg and require specialized print heads, but the performance advantages justify costs in demanding applications.
品質保証基準
Industrial applications demand consistent quality. Certifications indicate established processes rather than marketing claims.
ISO 9001:2015 certification indicates established quality management systems. Aerospace suppliers require AS9100D certification. Medical device manufacturers need ISO 13485 compliance. These aren’t optional for regulated industries—they’re entry requirements.
イーセン精密 maintains ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, ISO 14001, and IATF 16949 certifications, ensuring quality across diverse industries. These certifications mean documented processes, regular audits, and continuous improvement programs.
First Article Inspection reports, material certifications, and dimensional inspection data should accompany production parts. This documentation proves compliance and supports traceability requirements in regulated industries.
主な選考基準
Choosing appropriate large 3D printing services requires evaluating several factors that interact in complex ways.
Build volume requirements set the starting point. Measure maximum part dimensions including any supports. Parts exceeding available build volume require segmentation and assembly—possible but adding complexity.
Material properties needed narrow options quickly. Mechanical strength, temperature resistance, and chemical compatibility eliminate unsuitable processes. Match requirements to material datasheets rather than making optimistic assumptions.
Quantity and timeline influence technology choice. Single prototypes tolerate longer print times. Production runs need faster processes. Rush projects pay premium pricing—factor that into decision economics.
Surface finish expectations determine post-processing scope. As-printed finishes vary dramatically between technologies. エスエルエー delivers smooth surfaces. 多重伝送装置 shows visible layer lines. Budget time and money accordingly.
公差要件 determine if post-machining becomes necessary. Additive processes achieve certain precision limits. Tighter specifications require CNC加工サービス intervention.
Budget constraints ultimately limit options. Balance cost against performance needs. Sometimes good enough delivers better value than perfect.
Service providers offering multiple technologies provide flexibility. Access to both additive and CNC加工サービス capabilities under one roof streamlines production and simplifies project management.
Future Technology Trends
Markets and Markets forecasts continued innovation through 2030. Several developments show genuine promise rather than hype.
Multi-material printing enables simultaneous printing with different materials in single builds. Imagine printing rigid structural elements and flexible hinges in one operation. Early systems demonstrate the concept; broader adoption awaits material development and software refinement.
Increased automation through robotics integration reduces operator involvement. Automated part removal, support breakaway, and quality inspection accelerate throughput while improving consistency. Labor costs drive this trend—machines work continuously without fatigue.
AI-driven optimization applies machine learning to improve print quality and speed. Algorithms predict and prevent failures before they occur. Software suggests optimal orientations and support strategies. These tools evolve rapidly as training datasets expand.
Sustainable materials including recycled and biodegradable filaments gain adoption. Environmental concerns push development, while performance improvements make green materials competitive. The construction sector shows remarkable growth here—the 3D printing construction market reached $53.9 million in 2024, expanding at 111.3% annually according to industry analysis.
結論
Large 3D printing services continue transforming industrial manufacturing. The technology excels at producing complex geometries, reducing part counts, and accelerating development cycles. Market growth from $28.5 billion in 2024 toward $125.9 billion by 2033 reflects expanding adoption across industries.
Success requires matching technology to application requirements rather than forcing square pegs into round holes. Large format 3D printers offer distinct advantages for specific use cases. Integration with CNC加工サービス capabilities often delivers optimal results, combining additive manufacturing’s design freedom with subtractive precision.
Manufacturers evaluating these technologies should consider build volume needs, material requirements, quality standards, and whether hybrid approaches suit their applications. The right combination of additive and traditional manufacturing creates competitive advantages in today’s fast-paced markets.
What maximum size can large format 3D printers produce?
Build volumes vary by technology. FDM systems commonly reach 36″ x 24″ x 36″, with some industrial units printing up to 10 feet in length. Metal DMLS printers typically max out around 9″ x 9″ x 9″ per build. Larger parts require bonding multiple printed sections together.
How do costs compare between 3D printing and CNC machining?
For low volumes (1-100 units), large 3D printing services cost 40-70% less than traditional manufacturing when including tooling expenses. High volumes favor conventional methods. Hybrid approaches combining both technologies often provide optimal cost-performance balance for complex parts.
Can printed parts match traditionally manufactured strength?
Yes, when properly designed. Print orientation critically affects strength—parts can be 30-50% weaker when loaded perpendicular to layer lines. Materials like carbon fiber nylon and DMLS metals match or exceed conventional manufacturing strength in appropriate orientations with correct design.
What industries benefit most from large format printing?
Aerospace leads adoption, with the sector reaching $3.53 billion in 2024. Automotive manufacturing holds 25% market share. Healthcare, construction, and marine industries show strong growth. Any sector requiring large custom parts or rapid prototyping benefits significantly.
Ready to explore large format 3D printing for your manufacturing needs? Yicen Precision offers comprehensive additive manufacturing combined with precision CNC machining services, providing complete solutions from prototype to production.
参考文献
[1] IMARC Group. (2024). “3D Printing Market: Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2025-2033.” Retrieved from https://www.imarcgroup.com/3d-printing-market
[2] Fortune Business Insights. (2024). “Aerospace 3D Printing Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis, By Offerings (Printers, Materials, Software and Services), By Printer Technology, By Application, and Regional Forecast, 2024-2032.” Retrieved from https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/aerospace-3d-printing-market-101613
[3] Precedence Research. (2025). “3D Printing Market Size, Share, and Trends 2025 to 2034.” Retrieved from https://www.precedenceresearch.com/3d-printing-market
[4] MarketsandMarkets. (2024). “3D Printing Market by Offering (Printer, Material, Software, Service), Process (Binder Jetting, Direct Energy Deposition, Material Extrusion, Material Jetting, Powder Bed Fusion), Application, Technology, Vertical and Region – Global Forecast to 2030.” Retrieved from https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/3d-printing-market-1276.html
[5] Mordor Intelligence. (2025). “Aerospace 3D Printing Market – Forecasts from 2025 to 2030.” Retrieved from https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/3d-printing-in-aerospace-and-defense-market